Biology
Explore Biology
Dr. Archana Thakur | A Novel Immunotherapy Approach to Treat Solid Tumors
Developing therapies to effectively treat cancerous tumors is challenging, due to the hostility of the tumor microenvironment and the potential to unintentionally damage surrounding tissues. Infusions of immune cells can improve immune function and assist the body in fighting disease, although this approach increases the risk of inducing dangerous inflammatory responses. Dr. Archana Thakur and her colleagues at the Universities of Virginia and Pennsylvania have engineered a pioneering immunotherapy system that precisely targets cancerous cells. This new immunotherapy poses minimal risk of adverse reactions, and can be used against a wide range of tumor types.
Dr. Christopher Buck | Expanding Our Knowledge of Viral Evolution
Vitamin D has been studied as a treatment for a large number of diseases and conditions, from cancer to autism to COVID-19. However, its mode of action is not completely understood. Professor Ralf Herwig carries out his research at HG Pharma GmbH (Austria) and Ulster University (UK). His vital work explores the role of vitamin D in the body with a view to unlocking its potential as a treatment for a variety of health conditions involving the immune system.
Dr Katty Kang | Deciphering the Molecular Origins of Brain Disorders
During brain development, anomalies may arise which lead to serious conditions such as epilepsy, triggering seizures and requiring lifelong monitoring and medication. However, the underlying causes and the way in which these defects occur are not completely understood. Dr Katty (Jing-Qiong) Kang and colleagues at Vanderbilt University Medical Centre in the USA have conducted extensive research into the molecular mechanisms associated with developmental brain disorders, with a focus on genetic epilepsy. They propose novel therapeutic targets to effectively manage symptoms and improve clinical outcomes by targeting the root cause.
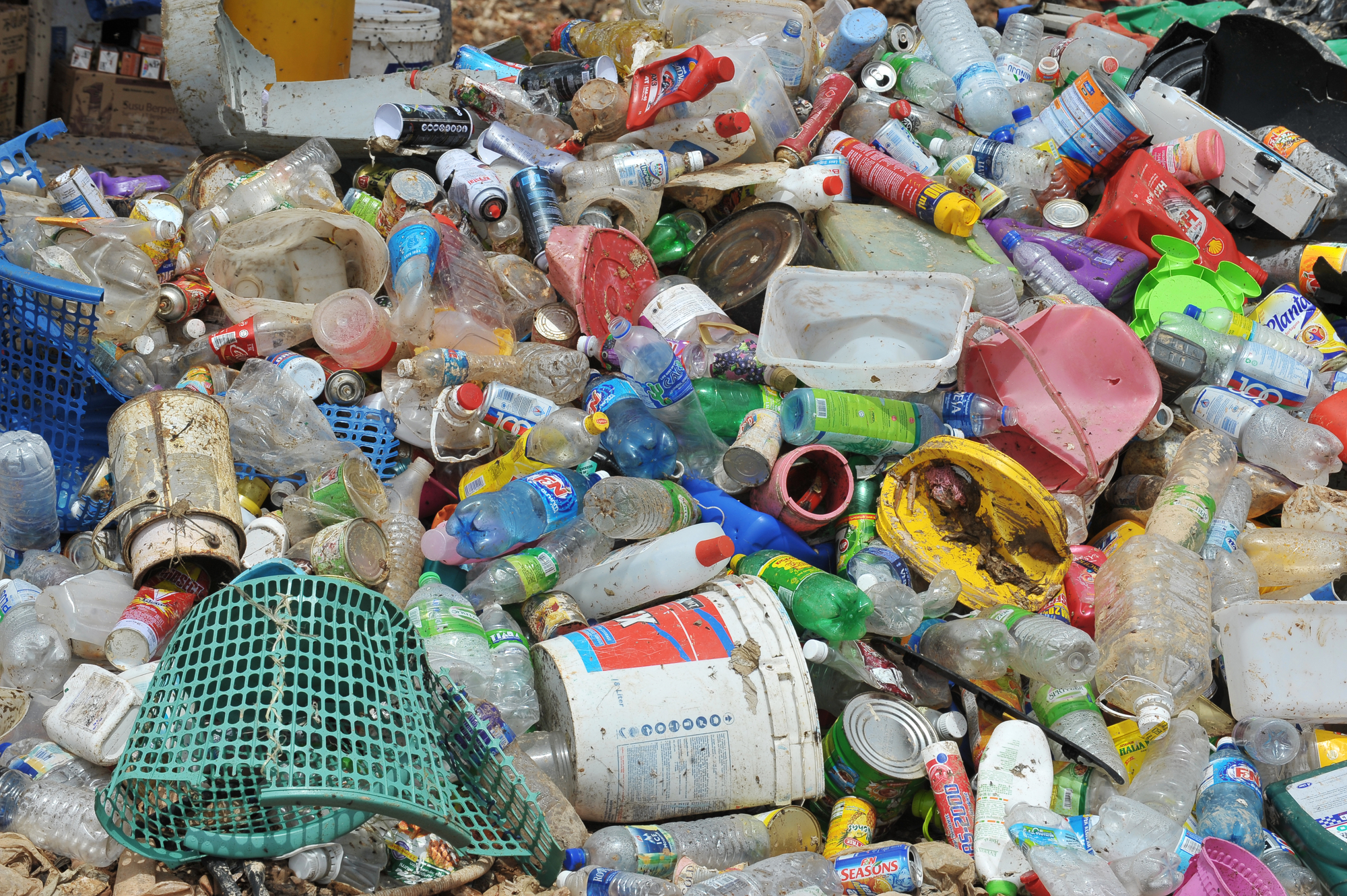

Dr Jay Mellies | Using Hungry Microbes to Devour Plastic Pollution
Plastic pollution is accelerating the destruction of our planet. Discarded plastic can be found in the remotest areas – from the highest mountain tops to the deepest ocean trenches. As many types of plastic take hundreds of years to break down, finding better solutions to the plastic crisis is vital. In recent research, Dr Jay Mellies from Reed College in Oregon examines the ability of microbes to break down mixed-plastic waste.
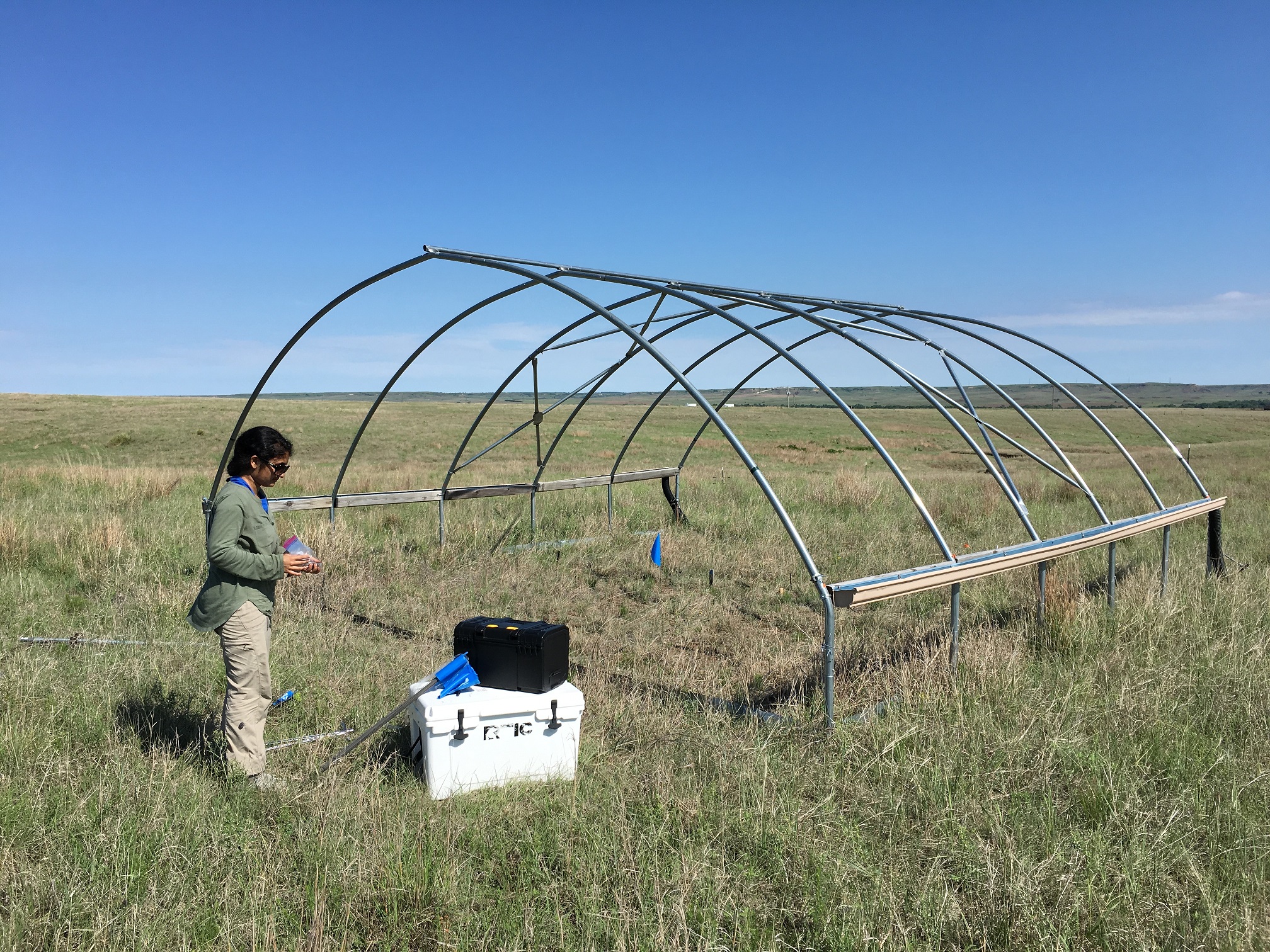

Dr Ari Jumpponen | Exploring How Soil Fungi Respond to Drought
Both the frequency and intensity of droughts are forecast to increase in climate change predictions. It is well established that plant communities are sensitive to drought conditions, having implications for agriculture, forestry, and wild habitats. Despite the close association between soil fungi and plants, our understanding of how fungal communities respond to drought remains incomplete. To build this understanding, Dr Ari Jumpponen and his colleagues at Kansas State University used a combination of pure culture- and DNA-based techniques to study soil fungal communities exposed to chronic drought conditions.
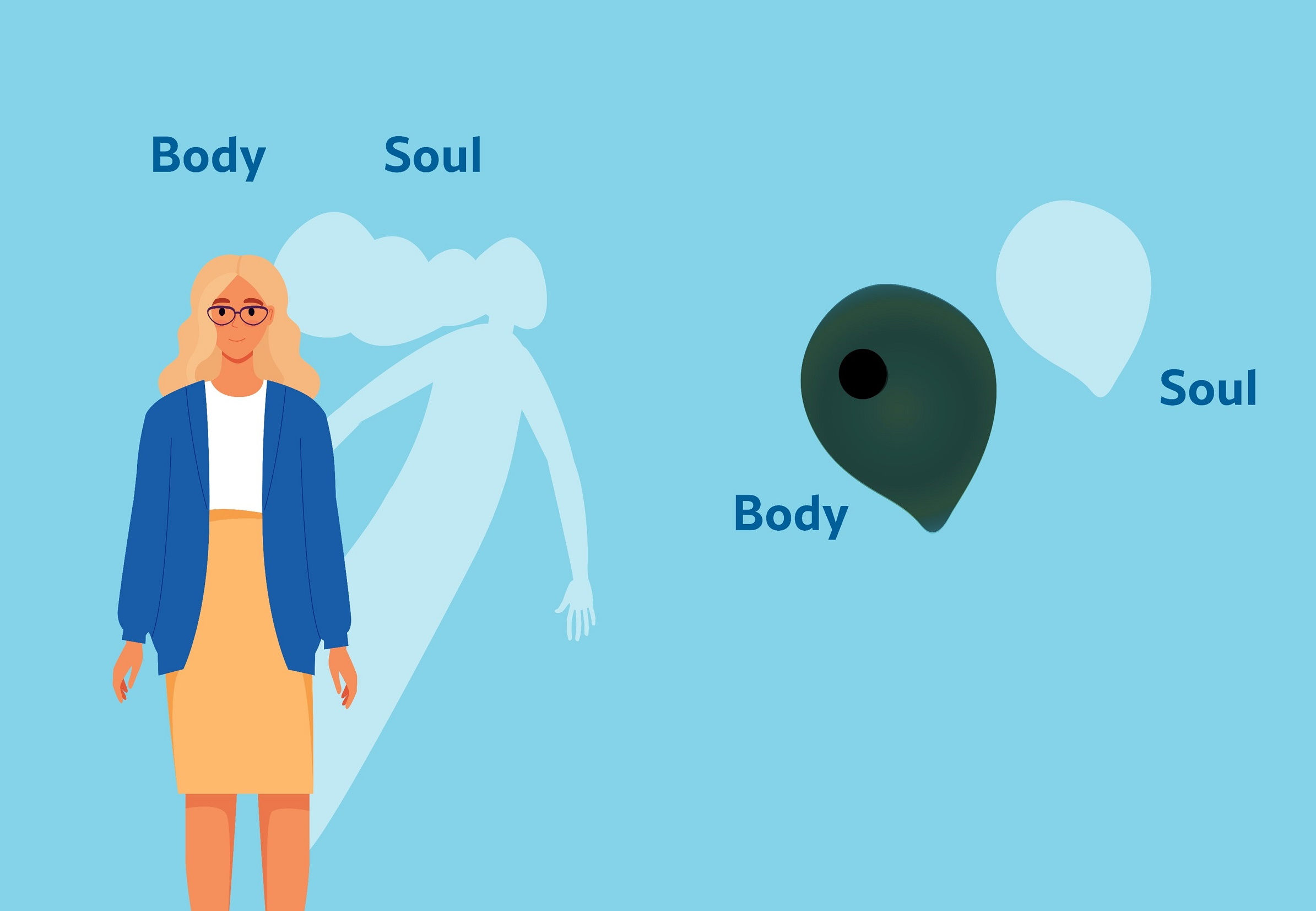
Dr Benjamin Scherlag | Could the Soul Be a Biophysical Reality?
The idea that human beings have souls that leave their body after death is an essential part of most religions and spiritual beliefs. However, this has been very difficult to prove scientifically. Benjamin Scherlag, Ronald Scherlag, Tarun Dasari and Sunny Po at the University of Oklahoma Health Science Centre recently investigated the existence of a soul by conducting a series of scientific studies. They carried out these experiments on a dwarf form of the organism Stentor coeruleus, which is known for its regenerative abilities.
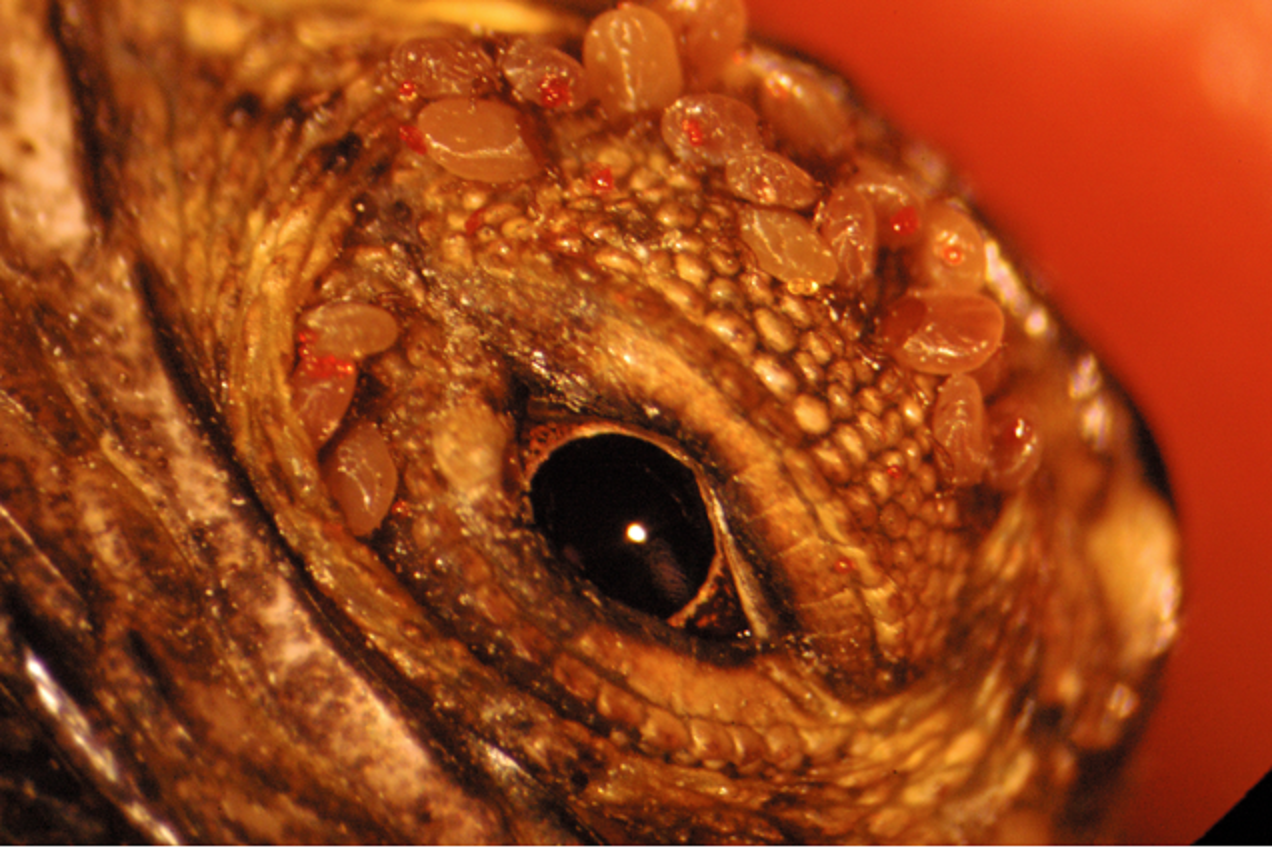
Dr Gita Kolluru | Dylan Lanser | Dr Larisa Vredevoe – Reproductive Consequences for Tick-Infested Lizards
Each year, male Western fence lizards bob, charge, and battle rivals for a chance to win mates. For many of them, tick infestations threaten to hinder their best efforts by harming the lizards’ health. But just how harmful is tick parasitism for these unfortunate lizard hosts? In their recent research, Dylan Lanser, Dr Larisa Vredevoe, and Dr Gita Kolluru at California Polytechnic State University aimed to answer this question by staging contests between tick-free and tick-infested lizards.
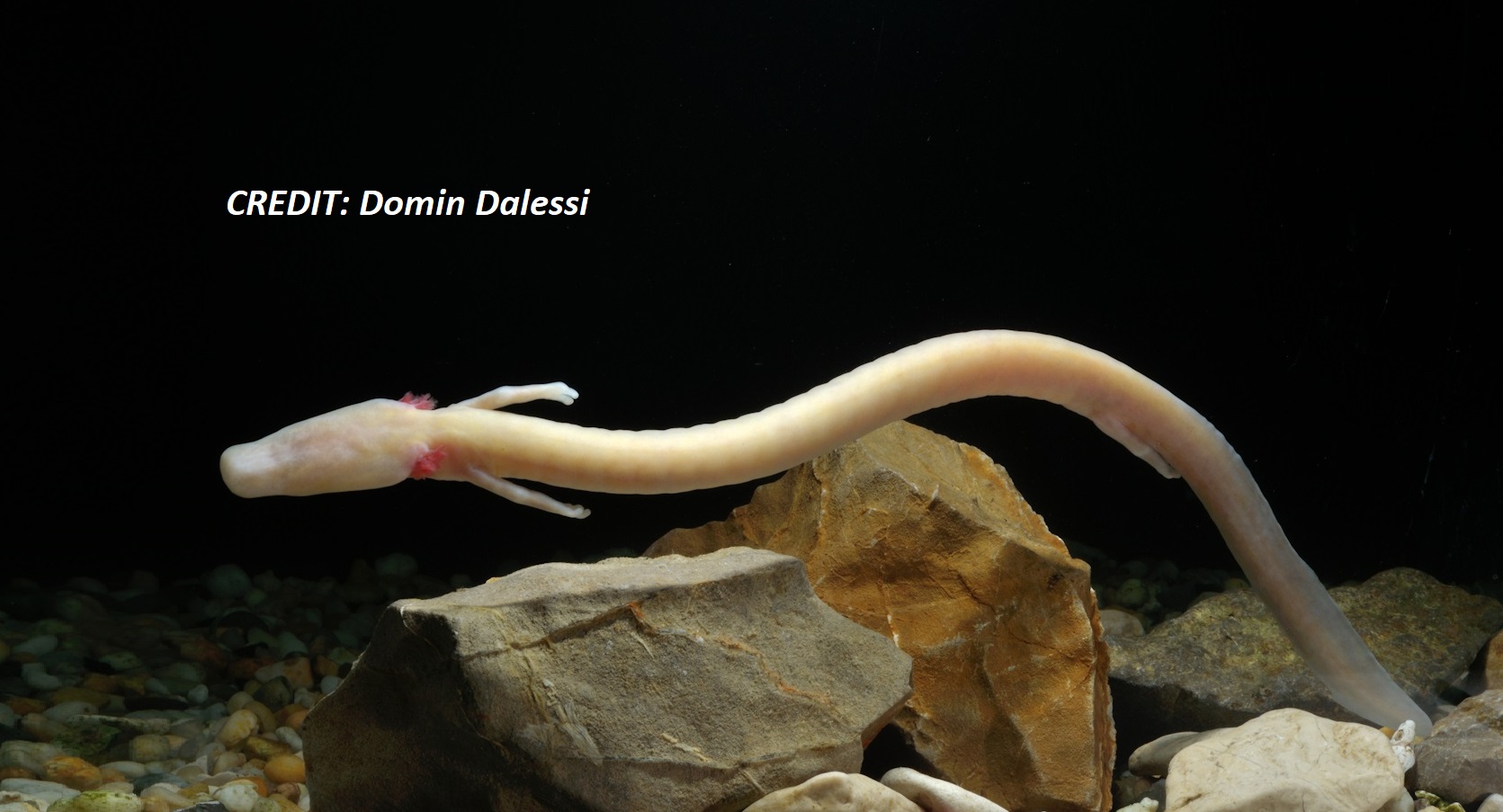

Dr Rok Kostanjšek | Revealing the Olm Salamander’s Secrets to Advance Biomedical Research
The genetic secrets to extraordinary longevity, superhero-like healing and regeneration, and resistance to feeding disorders could be found hidden within the Earth. In underground caves in Dinaric Karst along the Adriatic Sea in the Western Balkans lives a cave salamander, the olm, whose remarkable adaptations mean its genome holds great promise for biomedical research. Dr Rok Kostanjšek and an international team of scientists at the Proteus Genome Research Consortium are tackling the challenge of sequencing the huge olm genome, to provide the basis for studying its unique genetic characteristics.
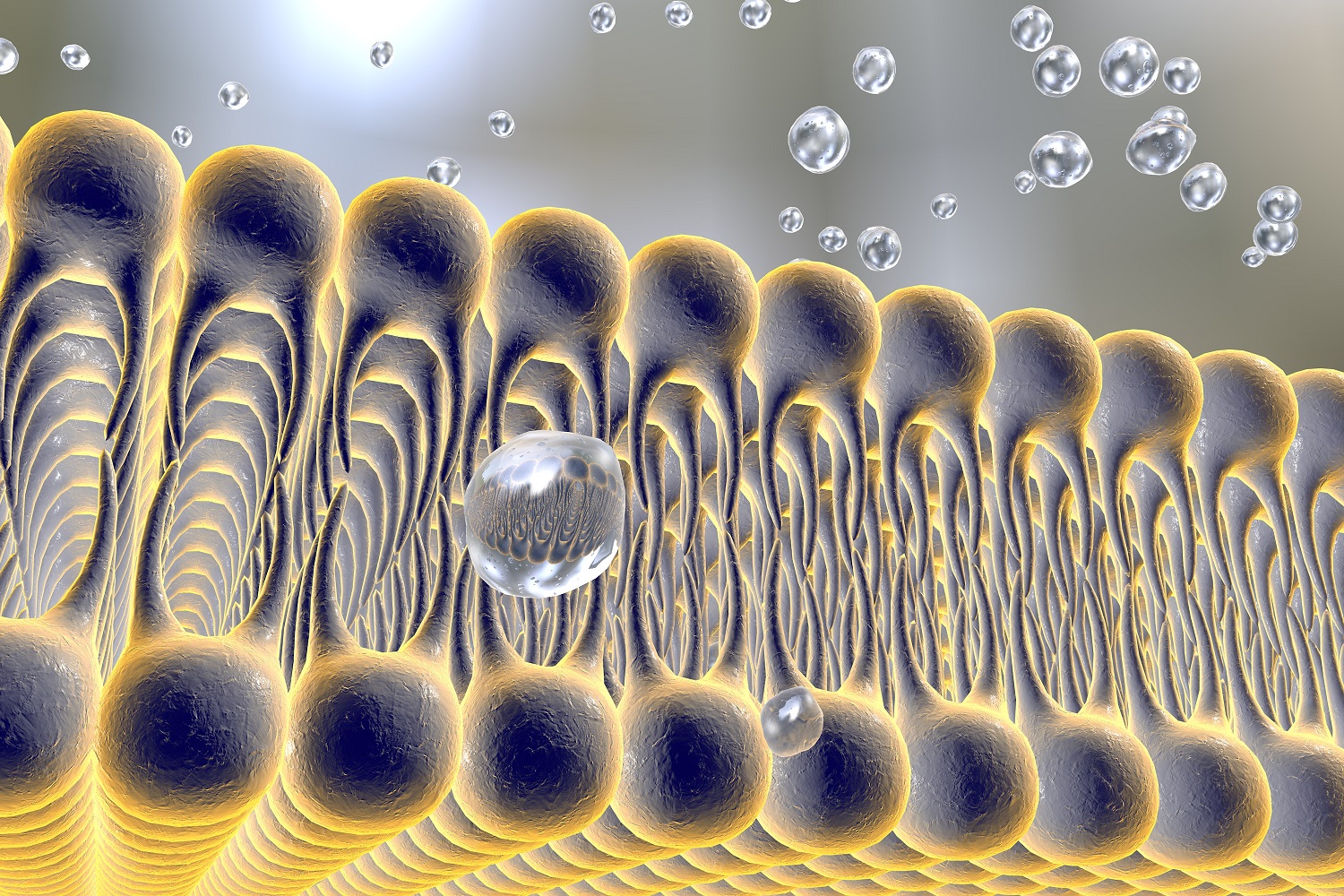
Dr Youzhong Guo | Accelerating Our Understanding of Cell Membranes
Cell membranes are critical for life. Effectively extracting proteins with naturally associated lipids from cell membranes is necessary for research, but traditional methods may damage these membrane components and limit the accuracy of scientific data. Dr Youzhong Guo at Virginia Commonwealth University has recently developed a revolutionary method for extracting membrane components in the form of Native Cell Membrane Nanoparticles. His team’s exciting work advances our understanding of the structure, function and interactions of membrane proteins and lipids.
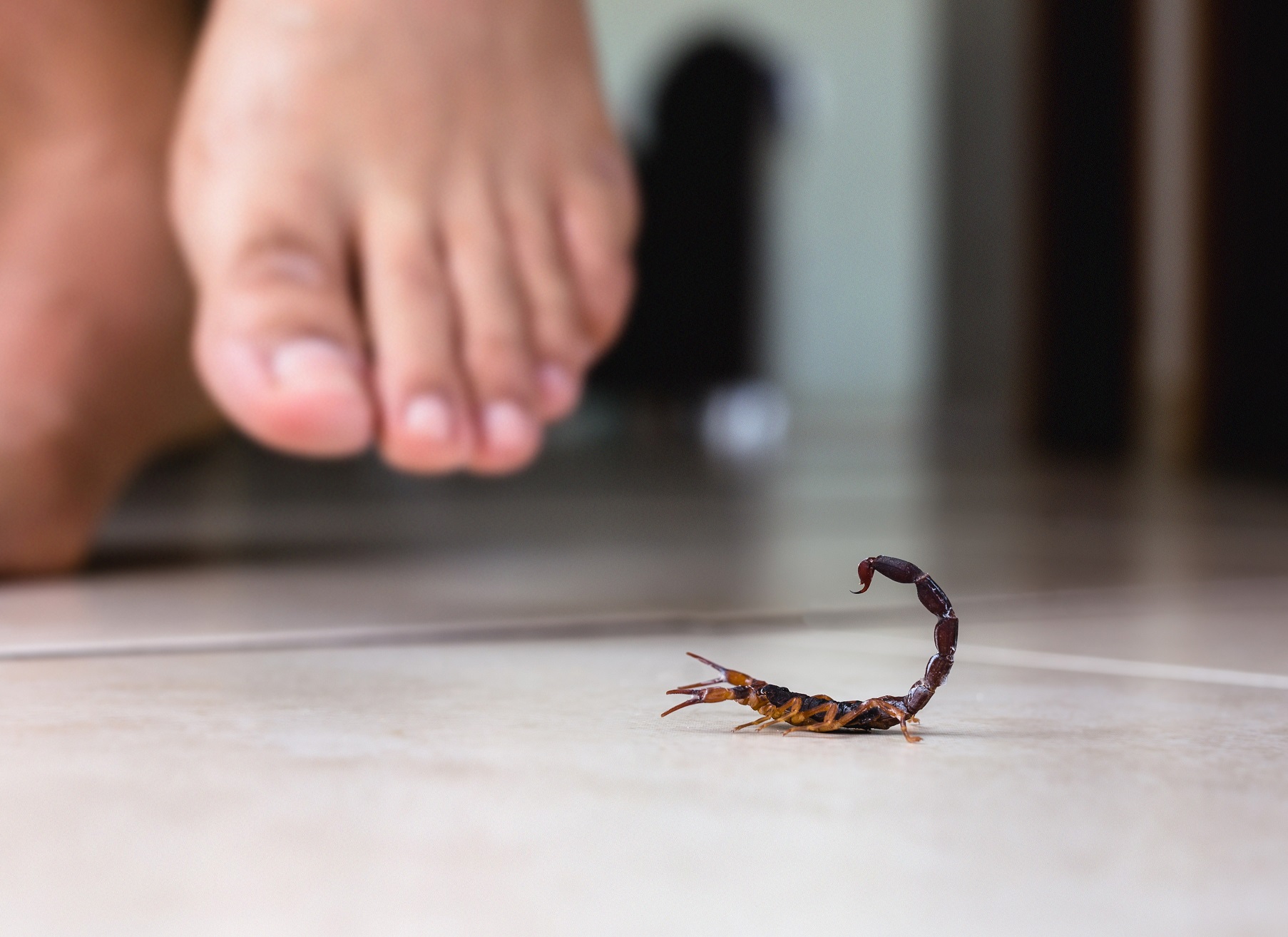

Dr Daniel Suiter – Dr Brian Forschler | Identifying and Preventing Arthropod Encounters in South-eastern USA Homes
Arthropods – a group of invertebrates that includes insects, spiders, centipedes and woodlice – are everywhere, and have inhabited this planet for millions of years. They are found in most habitats on Earth – including our gardens and homes. It is in these built environments that a small number are considered a nuisance when sharing our ‘sacred space’. An even smaller number damage buildings or belongings, eat our food – even feed on us – so we label them… pests! Successful management of pest populations requires an understanding of their specific lifestyles and their requirements for food, water, shelter, breeding sites, and favourable temperatures. A team of entomologists at the University of Georgia recently published a guidebook of more than 100 arthropods found in and around homes in the South-eastern USA.

Dr Attila Salamon | Dr John Kent – Double-Yolked Eggs: Egg-cellent or Egg-cident?
Eggs are marvellous – they contain all the sustenance needed to make a young bird within their protective shell, and when destined for the plate, they are nutritious and delicious. For many of us, cracking open an egg for breakfast to discover two yolks in the pan is a pleasant surprise. However, if eggs are nature’s miracle of packaging, then double-yolked eggs must be nature’s mistake – a mistake that still holds many mysteries. To answer some persisting questions, Dr Attila Salamon and Dr John Kent of University College Dublin examined our collective knowledge on double-yolked eggs in a recent review.

Dr Kahiu Ngugi | Developing Drought and Weed Resistant Super-Sorghum
Future food security is one of the key global challenges facing society. Climate change presents significant threats to our ability to produce staple food crops – particularly in regions already vulnerable to droughts. Dr Kahiu Ngugi and his research team from the University of Nairobi and other institutions in Kenya investigated numerous varieties of sorghum – one of the world’s most important cereal crops. Their aim was to find new genes that would allow the crop to withstand both drought and a common parasitic weed.
Increase The Impact Of Your Research!
Explore partnership opportunities
Unwind without the hassle. Enjoy fresh audiobooks, delivered free!
