Biology
Explore Biology

Exploring the Impact of Urbanisation on Soil Microbes | Dr Carl Rosier
Beneath our feet lies one of the most biodiverse habitats imaginable – the soil. These highly active underground microbial communities are vital to ecosystem health; they cycle nutrients, form soil structure, and decompose organic matter, among many other functions. The type of microbes that colonise soil is determined by the local plant community and climatic variables, both of which are rapidly changing due to human activity. In a recent study, Dr Carl Rosier of the University of Delaware has explored how urban development disturbs the environmental cycles that influence the types of microbes found in various soil habitats.

Investigating Fructans to Understand How Plants Can Survive Harsh Environments | Dr José Ordaz-Ortiz
The molecules within plant tissues can tell us about how they can withstand harsh environmental conditions. The Agave tequilana plant, native to Mexico, has a high concentration of fructan molecules throughout its tissues. Alongside his colleagues, Dr José Ordaz-Ortiz at the Center for Research and Advanced Studies of the National Polytechnic Institute in Mexico, combines several powerful analytical techniques to better understand the role that these fructans play in plant biology.

Understanding Sudden Unexpected Infant Death: A Unique Collaboration
When a supposedly healthy infant passes away, it can be hard to understand why. Juan Lavista Ferres (Microsoft), Dr Jan-Marino Ramirez and Dr Tatiana Anderson (both from Seattle Children’s Research Institute), and Professor Edwin Mitchell (University of Auckland), form the core of a novel collaboration to conduct vital and extensive research into the risk factors and mechanisms behind sudden unexpected infant death. This unique collaboration spanning across disciplines, industries and continents, is providing the deeper understanding that is needed to prevent unnecessary infant deaths.

Return of Baird’s Tapir: Blessing or Omen? | Dr LaRoy Brandt – Maggie Singleton
The destruction of jungle and forest habitats is a serious issue threatening species across the globe. Dr LaRoy Brandt and Maggie Singleton of Lincoln Memorial University studied one such threatened species, Baird’s tapir, in Costa Rica. By identifying the tapir’s tracks and deploying remote trail cameras, the team caught rare glimpses of this threatened species, indicating a return of the native population and an increase in their numbers. The question is, however, is this increase a sign of improving habitats or a result of less favourable forces at play?
How Cancer Cells Overcome the Obstacle of Senescence | Sebastian Igelmann
Cellular senescence [suh-NEH-Sns] is the process by which cells age and permanently stop dividing but do not die. While the process of senescence creates a barrier to tumour formation, it can still be overcome by cancer cells. Sebastian Igelmann, a PhD student supervised by group leader Dr Gerardo Ferbeyre at the University of Montreal, has identified a group of enzymes that work together to reprogramme cellular metabolism. This work provides important insight into how tumour cells may initiate proliferation and circumvent senescence. Critically, this specialist group of enzymes provides a potential therapeutic target for human cancer treatment.

The Holy Grail of Safer Opioids: Targeting Mu Opioid Receptor Splice Variants | Dr Ying-Xian Pan
Despite their numerous side effects, opioid drugs and morphine-like agents have remained a pillar in the medical management of pain. Most clinically used opioid drugs act through mu opioid receptors. Dr Ying-Xian Pan and his team from the Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, USA, studies the molecular and cellular mechanisms of mu opioid receptors and aim to develop novel strategies and opioid analgesics for better treating pain without side effects associated with traditional opiates. Efforts to find substitutes for traditional opioid drugs are helping address the opiate abuse crisis that affects many countries around the globe.

Using Genetics to Diagnose Rare Metabolic Diseases | Dr Michael Wanger
Identifying the cause of an illness in a sick baby or child is not always easy, particularly if the disease is rare. Throughout his career, Dr Michael Wangler, at the Baylor College of Medicine and Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute, has investigated rare childhood diseases. Combining his expertise in paediatrics and genetics, Dr Wangler utilises genomics, metabolomics and the humble fruit fly to identify the genes responsible for rare and undiagnosed diseases to improve both diagnosis and treatment.

Controlling the Worldwide chaotic Spreading of COVID-19 Through Vaccinations | Dr Aldo Bonasera
Amid the global COVID-19 pandemic, we face challenges that require innovative and strategic responding. Dr Aldo Bonasera at Texas A&M University in the USA and Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare in Italy, and Dr Hua Zheng at the School of Physics and Information Technology, Shaanxi Normal University in China, have taken a mathematical approach to compare the current COVID-19 pandemic with the Spanish Flu. Their findings have led to important recommendations for managing the current pandemic through vaccination programmes.
Exploring How Microbes Can Shed Light on Ancient Climate Conditions | Tor Einar Møller
To study the climate of the ancient past, researchers look for its fingerprints in deep marine and lake sediments. Within these geological records are large and active microbial communities that may hold other clues about past environmental conditions and transitions. Tor Einar Møller [Tore Ee-naar Moe-lerr], a doctoral candidate at the University of Bergen, Norway, examined the link between contemporary microbe composition and the ancient climate. In a recent paper, he demonstrates that current microbe communities found within sediment cores capture elements of past environments.

Improving Taxonomy Research for Enhanced Conservation and Collaboration
Identifying species with accuracy is important for numerous reasons; for instance, accurately knowing which organisms are present in an ecosystem is essential for informing conservation strategies to protect it. Therefore, if there is any question about an organism’s identity, it is important to document that uncertainty. However, levels of uncertainty are unknown for many research groups that carry out biological monitoring. James Stribling and Erik Leppo from Tetra Tech, Inc.’s Center for Ecological Sciences introduce a process for deriving uncertainty values, by studying the rates at which freshwater organisms in the US tend to be misidentified.
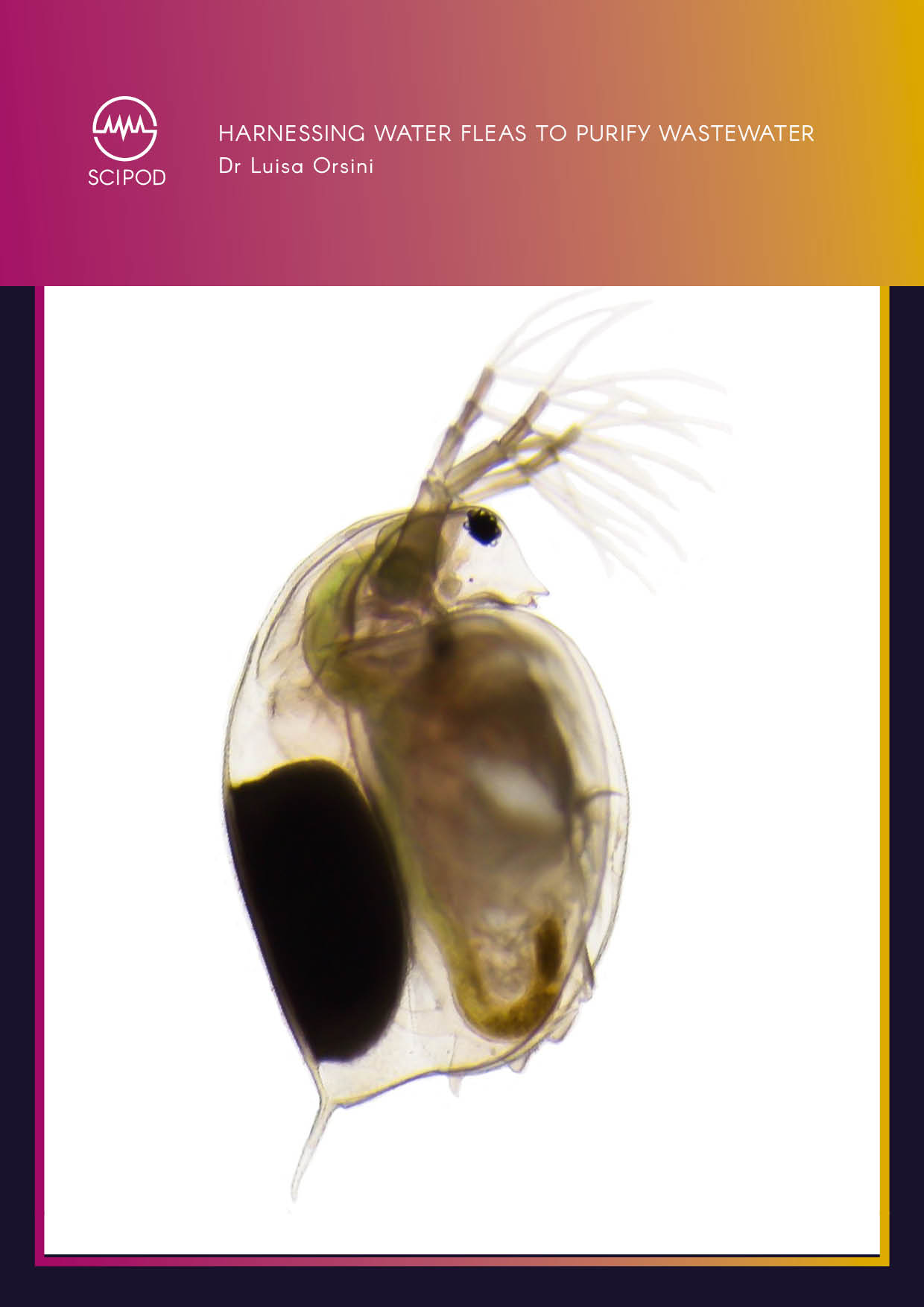

Harnessing Water Fleas to Purify Wastewater
Water-treatment processes are essential for water reuse in municipal, agricultural and industrial applications. Wastewater treatment ensures our safety and prevents sickness and death from parasites and contaminants every year. However, certain chemical contaminants, such as pharmaceuticals and pesticides, are difficult to remove from water, and can accumulate in the food web, eventually entering our food supply and potentially causing adverse health outcomes. Dr Luisa Orsini [Loo-ee-sah Oar-see-nee] and her colleagues at Daphne Water Solutions Ltd have developed a cutting-edge water-bioremediation technology, which is based on the use of small aquatic invertebrates called water fleas. By removing harmful contaminants from water, the sustainable and eco-friendly technology enables water reuse, while protecting human health and the environment.
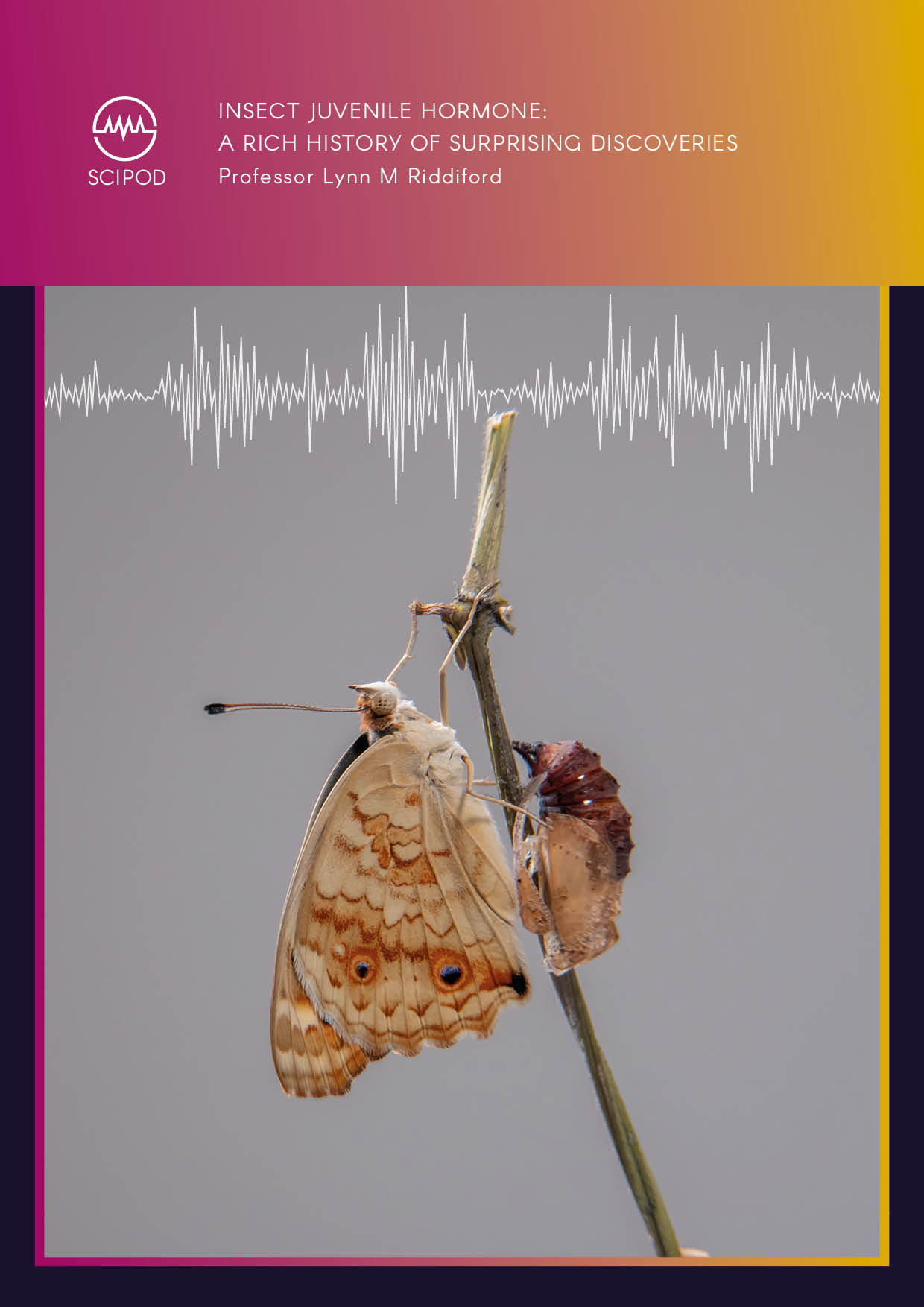

Insect Juvenile Hormone: A Rich History of Surprising Discoveries
The story of research into juvenile hormone, a fundamental chemical that regulates insect life history, follows the same thread as many other tales of scientific discovery. A series of serendipitous findings and observations led researchers to identify this unique hormone and isolate it from a moth. Additional studies focused on its potential as an insecticide, given that it has diverse effects on various aspects of insect physiology. In a recent review paper, Professor Lynn M Riddiford of the University of Washington details major developments in the history of juvenile hormone research.
Increase The Impact Of Your Research!
Explore partnership opportunities
Unwind without the hassle. Enjoy fresh audiobooks, delivered free!
