Physical Sciences
Explore Physical Sciences
Ahmed Alhindi – Dr. Meng-Sang Chew | Improving compliant mechanism designs with fuzzy logic
When they design mechanical systems, engineers first need to understand how they will behave using mathematical modelling tools that can simulate their movements. In recent years, they have increasingly explored the possibilities of ‘compliant’ mechanisms: highly flexible systems which are now being applied across numerous leading fields of technology. However, because their motions are often incredibly complex, engineers have so far found it difficult to recreate their behaviours in the mathematical tools needed to design them. Because they involve complex, nonlinear behaviour, designing compliant mechanisms has posed a long-standing challenge for engineers. While several advanced synthesis methods are now available, they’re often computationally intensive and can’t readily cope with the inevitable uncertainties in a system’s operating variables. In their latest research, Ahmed Alhindi and Dr. Meng-Sang Chew at Lehigh University, Pennsylvania, propose a novel approach that directly accounts for uncertainty in the design process. By reformulating widely used equations, their ‘dimensional synthesis’ method offers a streamlined yet powerful way to design compliant mechanisms under real-world, uncertain conditions.
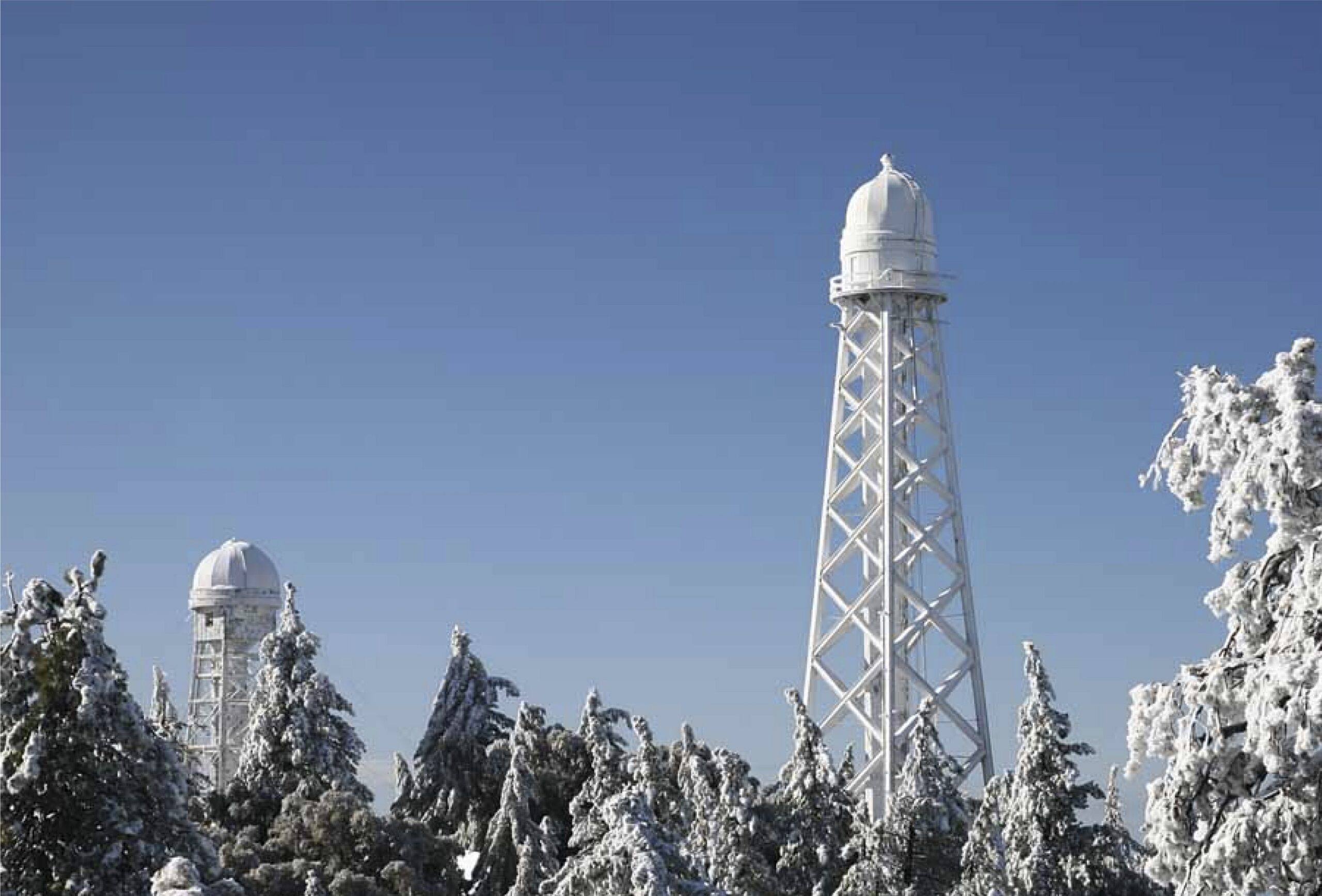

Professor Roger Ulrich | Revisiting Mount Wilson: How corrected solar data revealed a groundbreaking discovery
Between 1982 and 2012, the 150-foot solar tower at Mount Wilson Observatory collected a vast archive of observations of the Sun’s surface. In a series of recent studies, Professor Roger Ulrich, together with colleagues Dr. Tham Tran and Dr. John Boyden at UCLA, have revisited these data, running a thorough recalibration of the findings. Their results led them to a crucial discovery: two properties of the Sun’s plasma which were once thought to be separate are actually two faces of the same underlying effect, which plays a fundamental role in shaping the Sun’s magnetic field throughout the solar cycle.
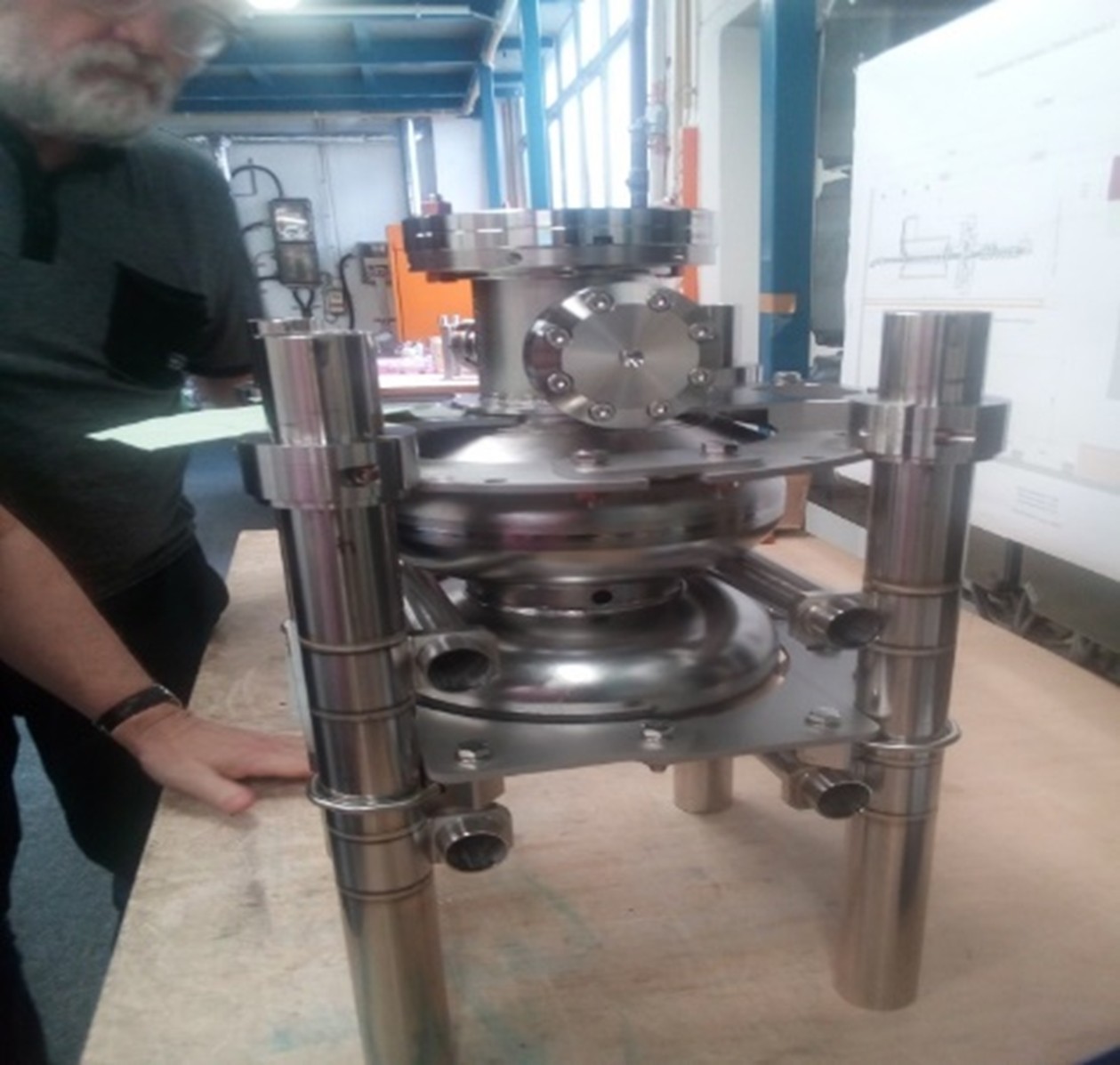

Dr Jerzy Lorkiewicz | How a Thin Film Could Transform the Future of Particle Accelerators
Building the next generation of particle accelerators depends on solving surprisingly small but stubborn material-related problems. Dr Jerzy Lorkiewicz and his collaborators of the National Centre for Nuclear Research in Poland tackled one of the toughest challenges: how to make lead films stick firmly to niobium, to realise his vision of a fully superconducting electron injector. By implanting lead ions into the niobium before adding a lead layer, his team created a smoother, more durable bond that resisted peeling. This innovation brings us closer to more efficient electron injectors for powerful particle accelerators.

Dr Michelangelo Anastassiades – Ann‑Kathrin Schäfer | A Smart Solution for Detecting Hidden Pesticides in Food
Highly polar pesticides such as glyphosate are notoriously difficult to detect in food due to their chemical properties and interference from natural food compounds. A new method developed by Dr Michelangelo Anastassiades and Ann‑Kathrin Schäfer of CVUA Stuttgart, and their colleagues, offers a more accurate and practical way to identify residues of these pesticides. By simplifying sample preparation and reducing interference, the method delivers reliable results across a wide range of foods. This development improves routine food safety testing and strengthens our ability to monitor potentially harmful pesticides.

Robert Nesbet | Universal conformal symmetry: Solution of the mysteries of cosmology?
For over a century, Einstein’s theory of general relativity has underpinned our understanding of gravity. However, it still hasn’t been able to explain some of the most enduring mysteries in cosmology, including the need for vast quantities of dark matter, which has gone undetected for decades. Today, this need has been explained by Conformal Gravity: a framework which modifies Einstein’s theory by requiring that the laws of physics must stay the same, even if all fields are scaled up or down at every point in space and time. Through his research, Robert Nesbet of IBM’s Almaden Research Center argues that this principle – named ‘universal conformal symmetry’ – should apply to all fundamental fields. If correct, this framework could eliminate the need for dark matter and dark energy.
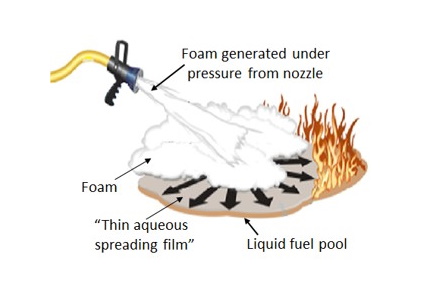
Dr. Arthur Snow | From Firefighting Foams to Molecular Mysteries: A Surfactant’s Unexpected Journey
Scientific discovery often unfolds in unexpected ways. What begins as a search for solutions to real-world challenges can lead researchers into unexplored scientific territory, where unconventional ideas emerge and spark debate. This dynamic was at the heart of research by Dr. Arthur W. Snow and Dr. Ramagopal Ananth in the Chemistry Division of the US Naval Research Laboratory. Their study aimed to address a pressing need: replacing fluorocarbon surfactants in firefighting foams. What they discovered would take them beyond firefighting applications and into fundamental questions about the nature of water itself.
Professor Jeremy Maurer | Building a seismic timeline of the Nippes earthquake
Sitting directly over a complex network of fault lines, Haiti is one of the most earthquake-prone nations on Earth. In 2021, the Nippes earthquake became the latest to devastate the country, and today, researchers are still piecing together the timeline of seismic events which unfolded during the earthquake. Through their research, Professor Jeremy Maurer and colleagues at Missouri University of Science and Technology have described how the Nippes earthquake originated, shifted, and ruptured a major fault line, triggering numerous ‘afterslip’ events in the following days.

Prof. Dr. Ralf Klessen | Reviewing the formation of the universe’s first stars
Before the universe was illuminated by stars, most of its observable matter existed in a roughly even distribution of hydrogen and helium. As these materials collapsed under their own gravity, they would have heated up, initially preventing them from collapsing further to densities high enough for stars to form. As part of a new review, Prof. Dr. Ralf Klessen and Prof. Dr. Simon Glover at Heidelberg University investigate the chemical mechanisms which enabled this primordial gas to cool and fragment to form the universe’s first generation of stars.

Dr. Zhe Su | Understanding the twisted tectonics of the Sichuan basin
The Sichuan basin in southern China is a region of deep geological and seismological complexity, which has so far prevented researchers from understanding its tectonic past. Through fresh analysis of previous observations, combined with the latest modelling techniques, a team led by Dr. Zhe Su at the National Institute of Natural Hazards, Beijing, suggests for the first time that the entire Sichuan basin is slowly rotating. Their result could explain the origins of one of the deadliest earthquakes in living memory, and could also help seismologists to better predict when earthquakes will strike the region in the future.

Professor Christophe Ley | Spotting relationships in complex angular datasets
Data involving angles can be found across a diverse array of scientific fields, but so far, the mathematical tools used to study them have often proved insufficient to detect the complex relationships between different angles within large datasets. Through its research, a team consisting of Professor Christophe Ley and Sophia Loizidou from the University of Luxembourg, Professor Shogo Kato from the Institute of Statistical Mathematics in Tokyo, and Professor Kanti Mardia from the University of Leeds, has developed a new model which overcomes many of these challenges: allowing the researchers to study relationships between three angles at once, as well as mixtures of angles and classical measurements on the line.

Dr. Chance Glenn | Could extreme electric fields make the warp drive a reality?
For decades, works of science fiction have explored how the universe’s most fundamental speed limit could be broken by warping the fabric of spacetime. Through his experiments, Dr. Chance Glenn, founder of Morningbird Space Corporation, believes he may have discovered how spacetime can be distorted by extreme electric fields, which can be easily created in the lab. If his theory is correct, it would mean that the concept of ‘warp drives’ which allow us to travel at faster than the speed of light could be more feasible than we once thought.

Dr. Robert Tomkowski | Investigating How Dimpled Surfaces Can Minimise Friction
Dimpled surfaces offer a useful and easily implementable way to reduce friction between lubricated surfaces as they slide over each other. Through cutting-edge simulations, Dr. Robert Tomkowski and colleagues at the KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Sweden explore how the microscale structures of surface dimples can be optimized to minimize friction. Their findings could help to reduce wear in mechanical systems, while also making them more energy efficient.
Increase The Impact Of Your Research!
Explore partnership opportunities
Unwind without the hassle. Enjoy fresh audiobooks, delivered free!
