Education and Training
Explore Education and Training

Dr. Shasha Cui | A Global Classroom for Dental Residents: How Virtual Education is Reshaping Dental Training Worldwide
When the COVID-19 pandemic arrived as an unexpected and unwelcome presence in our lives, it didn’t just disrupt our daily routines, it drastically changed how we learn, teach, and connect. For many healthcare professionals, including those in dentistry, this meant abandoning lecture halls and clinical classrooms for an unfamiliar and potentially daunting virtual teaching landscape. After all, no-one knew if this mandatory experiment in online teaching would work out. Yet from this unprecedented upheaval emerged an extraordinary opportunity to rethink how education is delivered globally, one that Dr. Shasha Cui of the Eastman Institute for Oral Health at the University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry, and her colleagues, seized with insight, innovation, and a keen eye toward the future.

Dr Malgorzata Trela – Dr Sophie Rutschmann | From Classroom to Conference: How a New Teaching Model Lets Students Step Inside the Scientific Community
When you imagine a scientific conference, you may picture rows of poster boards, bustling coffee breaks, and seasoned researchers discussing the latest data and research approaches. It can feel like a world reserved for insiders. Yet a recent study led by Dr Malgorzata Trela and Dr Sophie Rutschmann at Imperial College London argues that this lively professional gathering is precisely where tomorrow’s scientists ought to cut their teeth. Their paper, “Immunology in Practice: a modular framework to support Master of Science students’ conference attendance and engagement,” describes an educational project that turns a four-day professional congress into the beating heart of a master’s-level module, and in doing so, reshapes how students learn, network and even see themselves.

Dr. Sarah Hallen | The patient will see you all now: redesigning clinical learning for better outcomes
If you picture doctors making their daily rounds through hospital floors, you might imagine a single doctor standing by a bedside, examining a patient’s chart, or perhaps a group of doctors discussing a case right outside a patient’s room. However, the future of hospital care may well look more like a well-choreographed team effort, with doctors, nurses, pharmacists, students, and patients themselves, all in the same room, and all working as one team. This is exactly what Dr. Sarah Hallen and her colleagues at MaineHealth Maine Medical Center Portland envisioned when they created the iPACE model, short for Interprofessional Partnership to Advance Care and Education. Launched in 2017, this model is not just changing how doctors are trained; it’s leveraging team synergies to reshape what it means to deliver healthcare.
Professor Shanshan Yan | Heritage Language Learners Show Unique Advantages in Chinese Language Processing
Learning a new language as an adult is challenging, especially when the new language has features that differ significantly from one’s native tongue. This phenomenon is key to a new study led by Professor Shanshan Yan at Peking University, which examines how language learning is affected when learners encounter features in their second language that are similar to those in their first language.

Professor Gaetano Lotrecchiano | How can we ensure that scientists in collaborative teams work well together?
Americans generally celebrate the abstract principle of diversity but does this translate into the policies that they support and the friendships that they form? A new study from Prof. Neeraj Rajasekar of the University of Illinois Springfield, Prof. Evan Stewart of the University of Massachusetts and Prof. Douglas Hartmann of the University of Minnesota, examines this. Rajasekar and colleagues find inconsistencies between Americans’ support for diversity in principle versus their attitudes in their day-to-day lives. The findings reveal widespread gaps that exist across demographic groups, with implications for understanding public opinion and advancing diversity efforts in the United States.
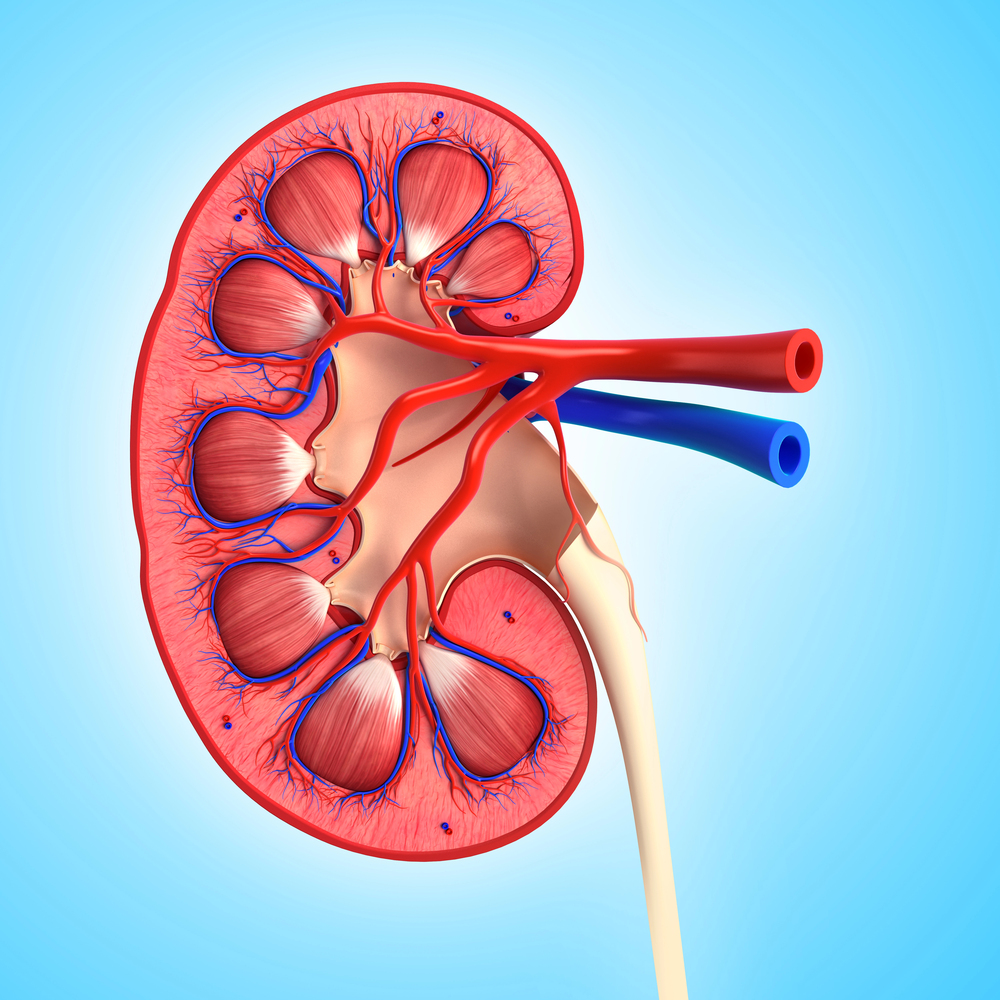
Dr. Serena Kuang | Inside the Kidney’s ‘Countercurrent’ Mystery: A New Model for Teaching and Studying Water Balance
Our kidneys filter blood to remove waste and can regulate water balance. We’ve all experienced that when we’re thirsty urine becomes concentrated, signalling us to drink more water. When we drink excess water, we urinate more frequently, and the urine is diluted. The kidneys’ ability to concentrate or dilute urine according to our body’s need relies on countercurrent multiplication (or CCM), a complex process that generates a salt concentration gradient in the kidney. However, CCM is challenging to teach and understand. Dr. Serena Kuang, a researcher and educator at Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine, has developed a more understandable CCM model and clears up errors in existing explanations making CCM easier to understand and teach.

Dr Elif Miskioğlu | Assessing the Value of Intuition for Solving Complex Engineering Problems
Experienced engineers are typically equipped with advanced technical knowledge and a unique professional skillset. These skillskets are often paried with impressive intuition, which allows engineers to devise solutions to complex real-world problems. Engineering faculty at Bucknell University, Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University, and The Ohio State University recently engaged in important research to further our understanding of intuition in engineering practice.

Dr David Mather | A Promising Approach to Prevent Children from Developing Dyslexia
Studies suggest that children who rely more on vision from their left eye could be more likely to develop dyslexia if they learn to write using pathways in the right brain hemisphere. Dr David Mather, a researcher at the University of Victoria, recently published a paper reviewing these findings. He outlines a proposed approach to teaching writing skills that could prevent these children from developing dyslexia. This approach involves teaching children to write when they are 7 or 8 years old, when the human brain is better at mapping and memorising entire words.

A Summer Opportunity Programme for Aspiring Scientists – with a Digital Twist
The development of a talent pool in Science Technology Education and Medicine that is as diverse as our population, has been a difficult goal for decades. Increasing the diversity of scientists from underrepresented communities can drive both innovation and creativity within the sciences. The Molecular & Environmental Toxicology Centre at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA, has run a summer research opportunity programme since 2011, providing scientific experiences and promoting scientific careers in the environmental health sciences for aspiring young people from backgrounds historically underrepresented in this field.

Dr Kristiina A. Vogt | Dr Samantha De Abreu | Dr Maria Blancas – Indigenous Holistic Storytelling to Teach Environmental Science
Western approaches to environmental science typically focus on existing and future issues, such as climate change, and technological solutions to these issues. While these frameworks have their value, they often set aside holistic perspectives on land management, coexistence with nature, and ecosystem preservation. Dr Kristiina A. Vogt, Dr Samantha De Abreu and Dr Maria Blancas at the University of Washington are exploring the potential of holistic storytelling practices common among Indigenous communities to teach environmental science in more effective ways.

Dr Barrett Caldwell | A New Learner-Centred Design for Online Engineering Courses
The COVID-19 pandemic forced many universities to deliver their courses online, exposing the limitations of remote learning strategies. Dr Barrett Caldwell and his team at Purdue University devised a new approach that could help to improve online courses in different engineering subjects. The approach builds on his experience while teaching and developing the ‘Perspectives on Systems Engineering’ course, which is part of the curriculum for the Systems Engineering program at Purdue University.

Dr Evelyn Cooper | Dr Candice Duncan – Improving Agriculture and Geoscience through Educational Initiatives
Addressing the skills shortage within scientific sectors requires a targeted approach for attracting and retaining students in STEM education. Summer Opportunities in Agricultural Research and the Environment (SOARE), SOARE: Strategic Work in Applied Geosciences (SWAG) and AgDiscovery, three innovative programs at the University of Maryland, provide a gateway for continued education, particularly for students who are traditionally under-represented in scientific fields. Implemented by Dr Evelyn Cooper, the success of the AgDiscovery and SOARE programs at the university has led to the inception of the new SOARE:SWAG program. Co-directed by Dr Candice Duncan, SOARE:SWAG focuses on students within geoscience disciplines.
Increase The Impact Of Your Research!
Explore partnership opportunities
Unwind without the hassle. Enjoy fresh audiobooks, delivered free!
