
by admin | Apr 26, 2023 | biology animated, earth and environment animated, health and medicine animated, research animated
Our brain’s network structure consists of many interconnected regions, each containing billions of neurons. Many neurons within one region fire electrical signals at the same time, in synchrony, and even neurons across different regions may synchronise. These are known as synchronous clusters. The collective firing of neurons in synchronous clusters is believed to create brainwaves. Brainwave measurements of patients with epilepsy have shown that during seizures, there can be episodes of excessive synchrony. The mechanisms behind these episodes are not well understood.
by admin | Apr 26, 2023 | health and medicine animated, research animated
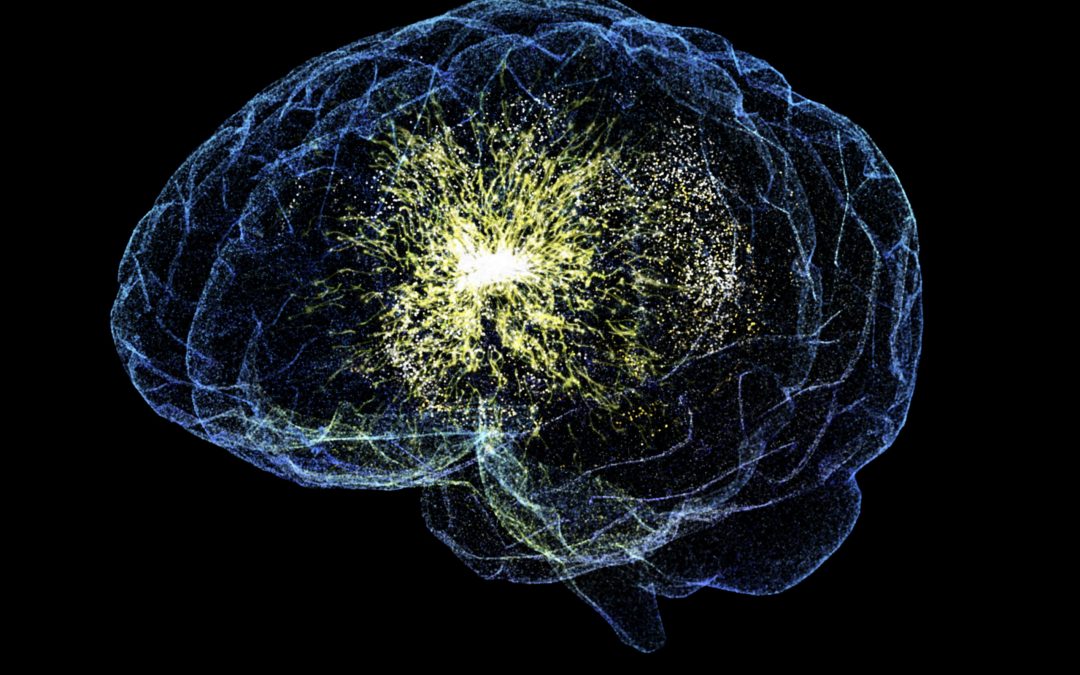
Our brain’s network structure consists of many interconnected regions, each containing billions of neurons. Many neurons within one region fire electrical signals at the same time, in synchrony, and even neurons across different regions may synchronise. These are known as synchronous clusters. The collective firing of neurons in synchronous clusters is believed to create brainwaves. Brainwave measurements of patients with epilepsy have shown that during seizures, there can be episodes of excessive synchrony. The mechanisms behind these episodes are not well understood.
by admin | Apr 20, 2023 | 3D animated, biology animated, health and medicine animated, research animated
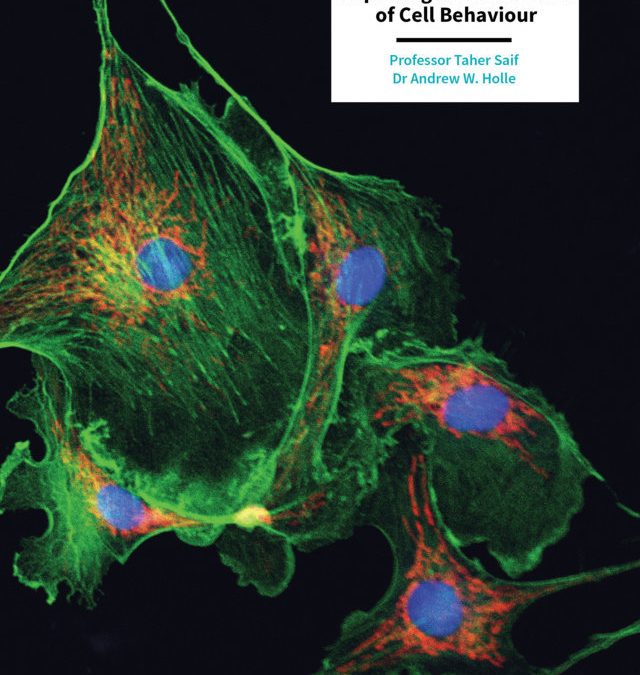
Extracellular biophysical cues have a profound influence on a wide range of cell behaviors, including growth, motility, differentiation, apoptosis, gene expression, adhesion, and signal transduction. Cells not only respond to definitively mechanical cues from the extracellular matrix (ECM) but can also sometimes alter the mechanical properties of the matrix and hence influence subsequent matrix-based cues in both physiological and pathological processes. Interactions between cells and materials in vitro can modify cell phenotype and ECM structure, whether intentionally or inadvertently. Interactions between cell and matrix mechanics in vivo are of particular importance in a wide variety of disorders, including cancer, central nervous system injury, fibrotic diseases, and myocardial infarction. Both the in vitro and in vivo effects of this coupling between mechanics and biology hold important implications for clinical applications.

by admin | Apr 19, 2023 | health and medicine animated, research animated
Divorce is commonplace but can have negative impacts on the cognitive, emotional, social and psychological development of children. Dr Stella Laletas of the Faculty of Education at Monash University explored the perspectives of teachers working with children in high-conflict divorce contexts. She makes critical recommendations to better support teachers involved in the education of vulnerable children.

by admin | Mar 15, 2023 | health and medicine animated, physical sciences animated, research animated
Nanotechnology offers exciting possibilities for the future of healthcare. Because of the tiny size of nano-devices, they are difficult to design and produce. Self-assembly, which involves taking simple structures and allowing them to combine to form larger, more complex structures, could be a solution to this problem. There are many examples of self-assembly in nature, such as the formation of DNA. Dr Florian Lau and his colleagues at the Institute of Telematics in Lübeck, Germany, research how to alter special building blocks of DNA – which they call ‘tiles’ – in such a way that allows them to self-assemble into ‘nanonetworks’.

by admin | Mar 8, 2023 | behavioural sciences animated, health and medicine animated, research animated
For young people with schizophrenia, their first experience of psychosis is often highly traumatic. Because of the close, nurturing relationships mothers typically have with their children, they too can experience trauma while witnessing their children’s disturbing psychotic episodes. As a result, mothers of adult children with schizophrenia often experience negative impacts on their physical and psychological health. Debra Klages takes a unique perspective by shedding light on how the traumatic experiences of health professionals with dual roles as mothers can lead to personal and professional growth and resilience.






