Revitalising Attention on the Global Asbestos Disaster – Dr Jukka Takala, et al.
Original Article Reference
This SciPod is a summary of the paper ‘Global Asbestos Disaster’, from the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15051000
Share Episode
About this episode
In developed countries, we are broadly aware of the dangers of asbestos and the risks it poses if discovered in our living or working environments. It may be shocking to learn that asbestos still causes an estimated 255,000 deaths annually worldwide, with the vast majority – 89% – from work-related exposure. Although asbestos is banned in 55 countries, it is still widely used in the developing world, and over two million tonnes are consumed annually, leading to what Dr Jukka Takala, President of the International Commission of Occupational Health, and an international team of authors describe as a global asbestos disaster.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. 
What does this mean?
Share: You can copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
Adapt: You can change, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
Credit: You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made.
Related episodes
Julius Reiff | Soil, Seeds, and Sustainability: The Power of Permaculture during Environmental Breakdown
Pressing environmental challenges, such as soil degradation, biodiversity loss, and climate change, can negatively affect agriculture, while also being driven by common agricultural practices. To tackle this predicament and ensure food security while promoting environmental sustainability, innovative agricultural practices are essential. Permaculture, a holistic approach to farming that mimics the stability and resilience of natural ecosystems, offers a promising solution. A recent study conducted by Julius Reiff of the Institute for Environmental Science, RPTU University of Kaiserslautern-Landau, Germany, and colleagues, provides compelling evidence of the benefits of permaculture in enhancing carbon stocks, improving soil quality, and boosting biodiversity.
Dr Alan Cottey | How we can Improve our Science Communication to Create Climate Crisis Action
We are facing a climate crisis that threatens our entire world and life as we know it. Despite this, scientists have found it difficult to engage people on the issue and inspire effective action. Dr Alan Cottey at the University of East Anglia explores the history of scientists’ climate warnings and suggests a four-register model of communication that he believes has the potential to reach people with varying degrees of scientific literacy and different lifestyles.
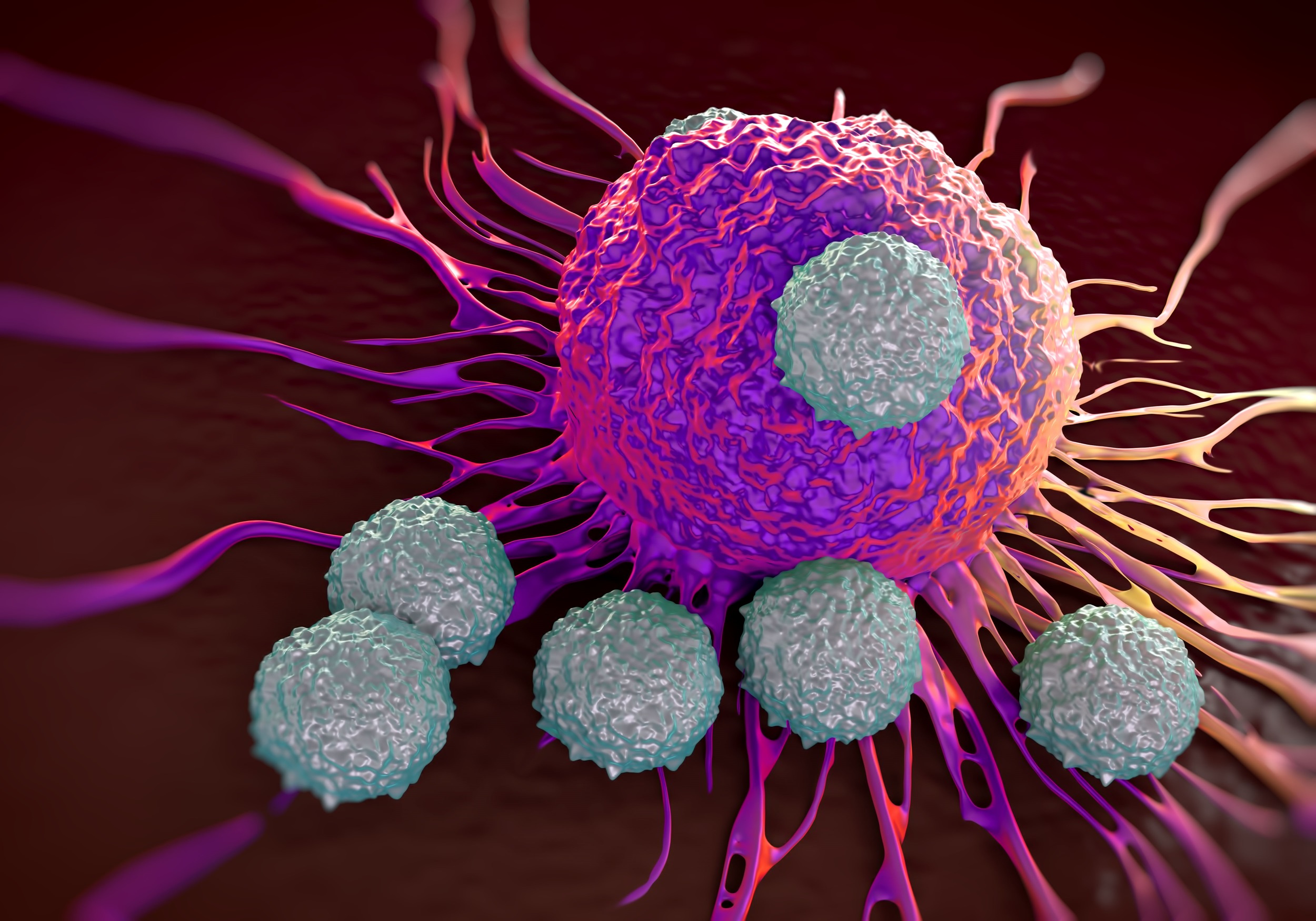
Dr. Archana Thakur | A Novel Immunotherapy Approach to Treat Solid Tumors
Developing therapies to effectively treat cancerous tumors is challenging, due to the hostility of the tumor microenvironment and the potential to unintentionally damage surrounding tissues. Infusions of immune cells can improve immune function and assist the body in fighting disease, although this approach increases the risk of inducing dangerous inflammatory responses. Dr. Archana Thakur and her colleagues at the Universities of Virginia and Pennsylvania have engineered a pioneering immunotherapy system that precisely targets cancerous cells. This new immunotherapy poses minimal risk of adverse reactions, and can be used against a wide range of tumor types.
Dr Eleanor Wilson | Breath by Breath: Decision-Making in the Final Stages of Motor Neurone Disease
Motor neurone disease is a currently incurable and progressive neurological disorder that severely impacts muscle function. As the disease progresses, individuals with motor neurone disease experience significant difficulties in movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing. Home mechanical ventilation can be used to support breathing and improve the quality of life. However, while this can alleviate symptoms and extend survival, it does not stop disease progression, and patients and caregivers must confront difficult decisions in their treatment journey. In a new UK study, Dr Eleanor Wilson of the University of Nottingham and colleagues have explored end-of-life decision-making in motor neurone disease patients using home mechanical ventilation.
Increase the impact of your research
• Good science communication encourages everyday people to be scientifically literate so that they can analyse the integrity and legitimacy of information.
• Good science communication encourages people into STEM-related fields of study and employment.
• Good public science communication fosters a community around research that includes both members of the public, policymakers and scientists.
• In a recent survey, 75% of people suggested they would prefer to listen to an interesting story than read it.

Step 1 Upload your science paper
Step 2 SciPod script written
Step 3 Voice audio recorded
Step 4 SciPod published