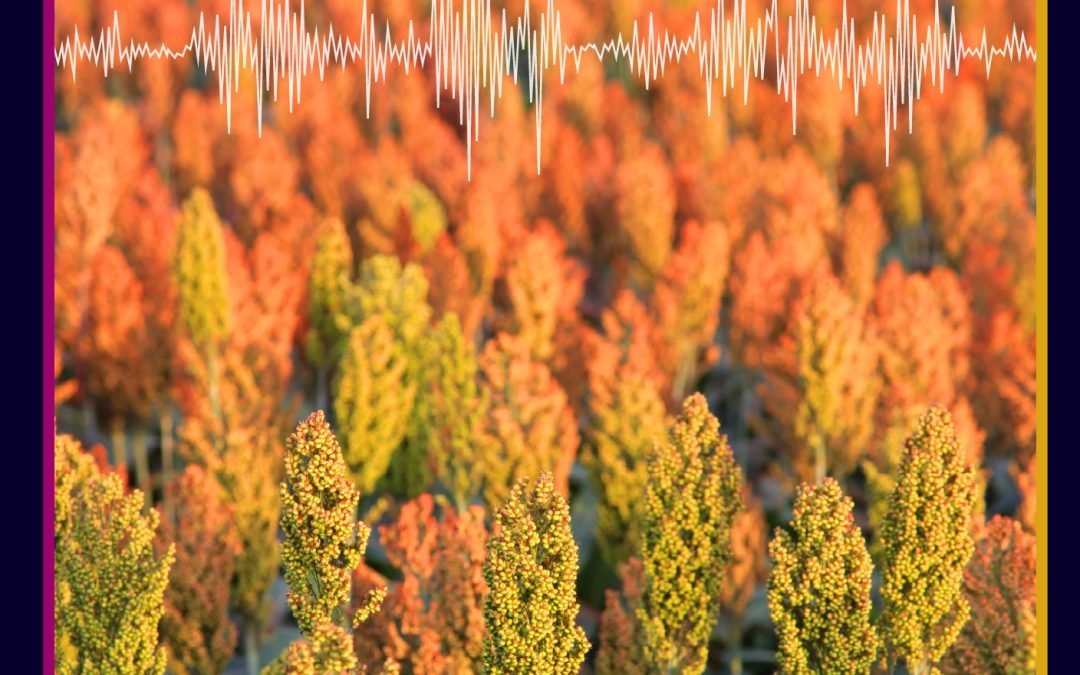

by admin | Jan 11, 2023 | biology, earth and environment
Future food security is one of the key global challenges facing society. Climate change presents significant threats to our ability to produce staple food crops – particularly in regions already vulnerable to droughts. Dr Kahiu Ngugi and his research team from the University of Nairobi and other institutions in Kenya investigated numerous varieties of sorghum – one of the world’s most important cereal crops. Their aim was to find new genes that would allow the crop to withstand both drought and a common parasitic weed.

by admin | Jan 11, 2023 | earth and environment
The Gold Rush of the 1800s is inextricably tied to USA history. Mining towns popped up wherever precious metals could be extracted, with many of these towns and mines now lying abandoned as ghostly reminders of the old wild west. Abandoned mine land poses a threat to environmental and human health, and methods to rehabilitate this land has gathered much interest over the past few years. Dr Carlos Rodriguez-Franco and Dr Deborah Page-Dumroese from the US Department of Agriculture have been evaluating the use of biochar as a sustainable method to remediate abandoned mine lands.

by admin | Jan 5, 2023 | earth and environment
The earth beneath our feet is far more than just dirt. Soil is a living ecosystem filled with microbes, worms and insects, and vast networks of underground fungi filaments. Healthy soils are critical to healthy ecosystems and productive agricultural systems. Dr Joji Muramoto and researchers from the University of California have created a framework for Integrated Soil Health Management that could help suppress plant diseases without the use of harmful chemicals.
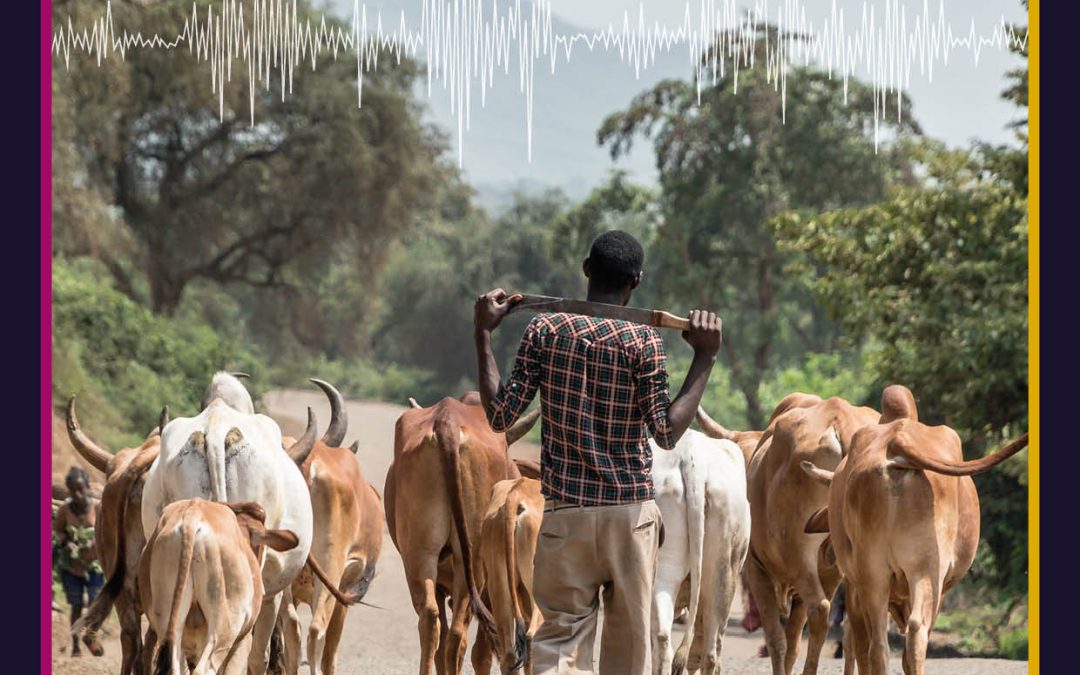

by admin | Dec 14, 2022 | earth and environment, Hindawi, social and behavioural sciences
Around the world, climate change is impacting the availability of food and water, affecting people’s health and livelihoods. Unfortunately, these damaging effects are more pronounced in developing countries. In a recent study, Dr Abera Habte of Wolaita Sodo University and his collaborators investigated the impacts of climate change in Southwestern Ethiopia. His team incorporated the perceptions and knowledge of local farmers into their analysis, in order to develop more effective climate adaptation strategies.
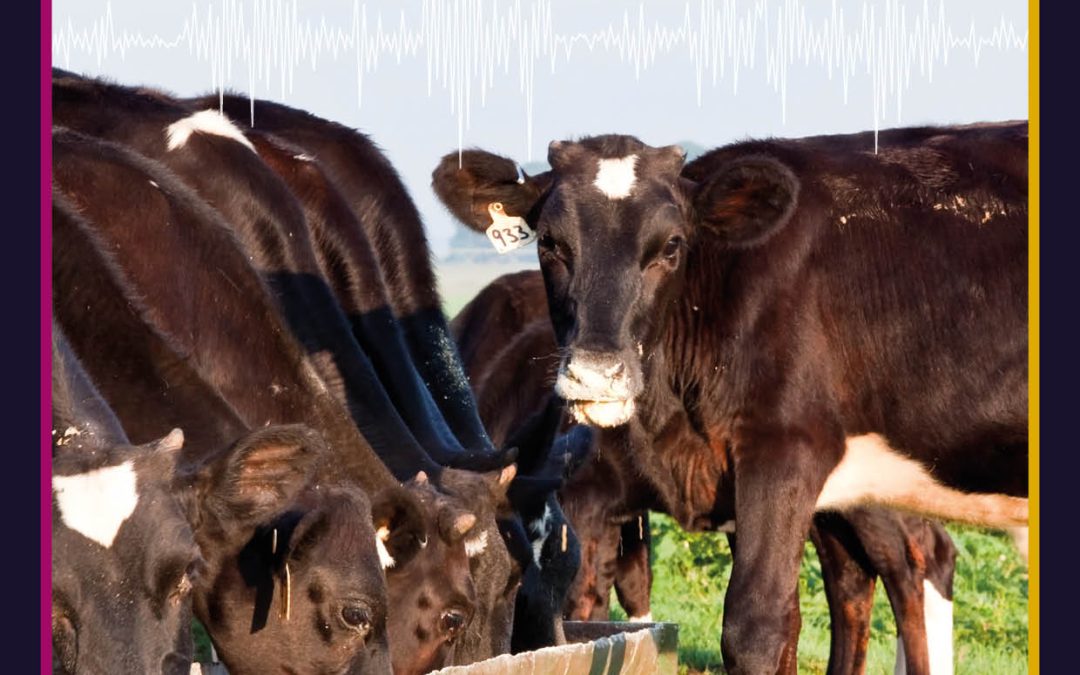

by admin | Dec 7, 2022 | biology, earth and environment
Methane is one of the most potent greenhouse gases that contributes to the global climate crisis. As this gas is produced in the digestive systems of cattle, methane represents one of the greatest problems faced by the farming industry. Dr Robert Bryant, Dr Langdon Martin and their team at Warren Wilson College, North Carolina, propose an innovative feed supplement for cattle that helps to significantly reduce methane emissions: waste yeast from craft breweries. If used on a large scale, this new supplement could significantly decrease emissions associated with cattle farming, while also creating a new use for a waste product of the craft beer industry.
by admin | Dec 7, 2022 | earth and environment
Savannas are characterised by the co-existence of two very different types of plants – trees and grasses. They may be open, with large swathes of grass and an occasional tree dotting the landscape, or closed with a near complete cover of trees and a sparse grass layer beneath. In drier parts of the world, drought may play an important role in determining the balance between the trees and grasses in savannas. Extreme droughts, which are likely to become more common with climate change, could permanently shift a closed savanna to an open one. Such changes would have significant consequences for the functioning of these ecosystems and the animals they support. Dr Anthony Swemmer of the South African Environmental Observation Network explored the impact of an unusually severe drought on trees in South Africa. His team’s research shows that the response of trees to drought depends on a suite of local factors.






