A Greener Future: Leveraging Ecosystem Services in Sustainable Landscape and City Management – Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology
Jun 1, 2018earth and environment
As global climate change and other major environmental threats advance, scientists are looking for ways to evaluate sustainable solutions for energy, agriculture and city management. Ecosystem services are benefits provided to humans by nature, and over the past two decades researchers have begun refining ways to assess the value of these services compared to human-made options. Dr Benedetto Rugani and his team are developing novel ways to assess ecosystem services and advance the use of nature-based solutions in urban areas.

You may also like …
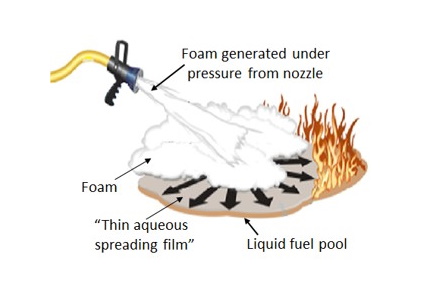
Dr. Arthur Snow | From Firefighting Foams to Molecular Mysteries: A Surfactant’s Unexpected Journey
Scientific discovery often unfolds in unexpected ways. What begins as a search for solutions to real-world challenges can lead researchers into unexplored scientific territory, where unconventional ideas emerge and spark debate. This dynamic was at the heart of research by Dr. Arthur W. Snow and Dr. Ramagopal Ananth in the Chemistry Division of the US Naval Research Laboratory. Their study aimed to address a pressing need: replacing fluorocarbon surfactants in firefighting foams. What they discovered would take them beyond firefighting applications and into fundamental questions about the nature of water itself.
Professor Jeremy Maurer | Building a seismic timeline of the Nippes earthquake
Sitting directly over a complex network of fault lines, Haiti is one of the most earthquake-prone nations on Earth. In 2021, the Nippes earthquake became the latest to devastate the country, and today, researchers are still piecing together the timeline of seismic events which unfolded during the earthquake. Through their research, Professor Jeremy Maurer and colleagues at Missouri University of Science and Technology have described how the Nippes earthquake originated, shifted, and ruptured a major fault line, triggering numerous ‘afterslip’ events in the following days.

Prof. Dr. Ralf Klessen | Reviewing the formation of the universe’s first stars
Before the universe was illuminated by stars, most of its observable matter existed in a roughly even distribution of hydrogen and helium. As these materials collapsed under their own gravity, they would have heated up, initially preventing them from collapsing further to densities high enough for stars to form. As part of a new review, Prof. Dr. Ralf Klessen and Prof. Dr. Simon Glover at Heidelberg University investigate the chemical mechanisms which enabled this primordial gas to cool and fragment to form the universe’s first generation of stars.
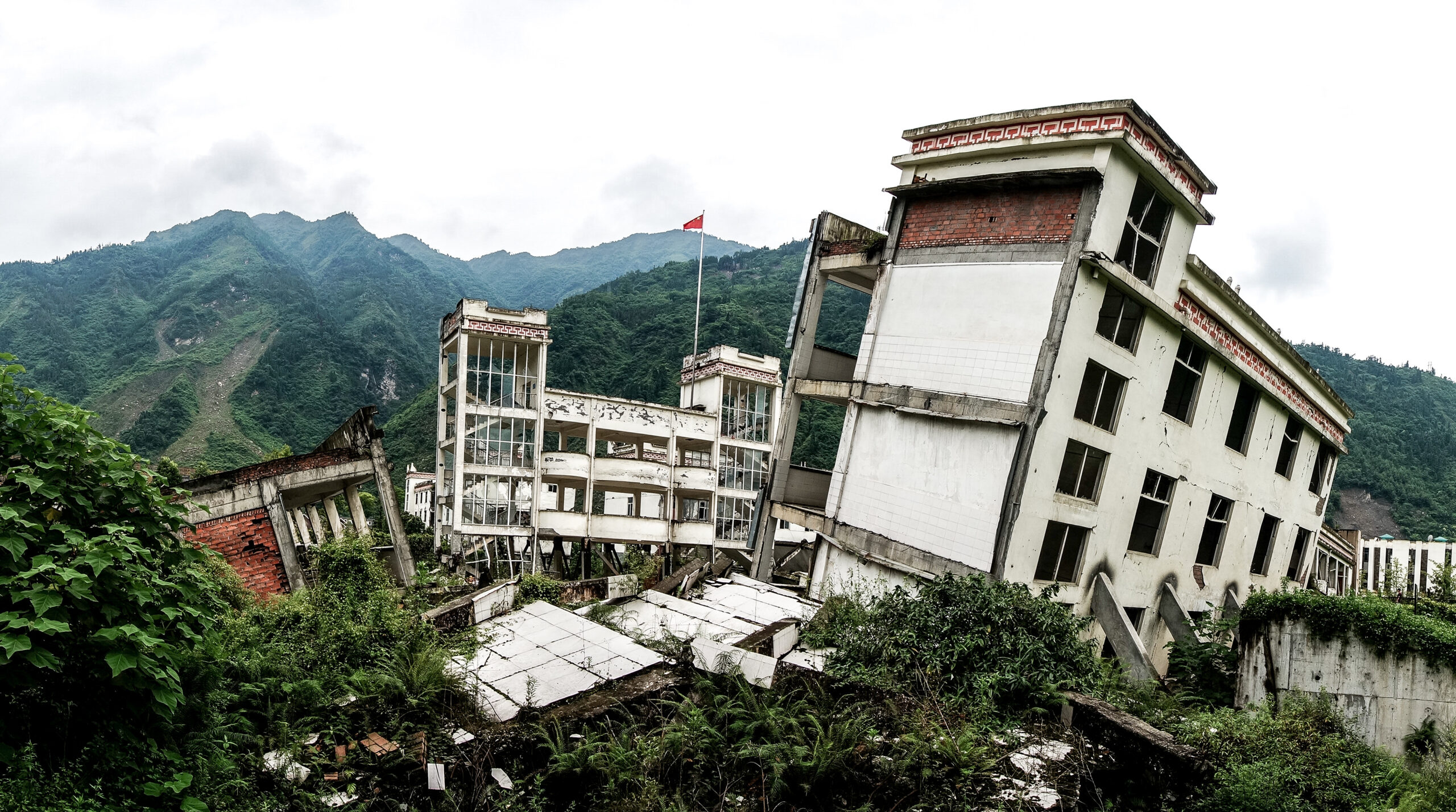

Dr. Zhe Su | Understanding the twisted tectonics of the Sichuan basin
The Sichuan basin in southern China is a region of deep geological and seismological complexity, which has so far prevented researchers from understanding its tectonic past. Through fresh analysis of previous observations, combined with the latest modelling techniques, a team led by Dr. Zhe Su at the National Institute of Natural Hazards, Beijing, suggests for the first time that the entire Sichuan basin is slowly rotating. Their result could explain the origins of one of the deadliest earthquakes in living memory, and could also help seismologists to better predict when earthquakes will strike the region in the future.

Professor Christophe Ley | Spotting relationships in complex angular datasets
Data involving angles can be found across a diverse array of scientific fields, but so far, the mathematical tools used to study them have often proved insufficient to detect the complex relationships between different angles within large datasets. Through its research, a team consisting of Professor Christophe Ley and Sophia Loizidou from the University of Luxembourg, Professor Shogo Kato from the Institute of Statistical Mathematics in Tokyo, and Professor Kanti Mardia from the University of Leeds, has developed a new model which overcomes many of these challenges: allowing the researchers to study relationships between three angles at once, as well as mixtures of angles and classical measurements on the line.

Dr. Chance Glenn | Could extreme electric fields make the warp drive a reality?
For decades, works of science fiction have explored how the universe’s most fundamental speed limit could be broken by warping the fabric of spacetime. Through his experiments, Dr. Chance Glenn, founder of Morningbird Space Corporation, believes he may have discovered how spacetime can be distorted by extreme electric fields, which can be easily created in the lab. If his theory is correct, it would mean that the concept of ‘warp drives’ which allow us to travel at faster than the speed of light could be more feasible than we once thought.

Dr. Robert Tomkowski | Investigating How Dimpled Surfaces Can Minimise Friction
Dimpled surfaces offer a useful and easily implementable way to reduce friction between lubricated surfaces as they slide over each other. Through cutting-edge simulations, Dr. Robert Tomkowski and colleagues at the KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Sweden explore how the microscale structures of surface dimples can be optimized to minimize friction. Their findings could help to reduce wear in mechanical systems, while also making them more energy efficient.

Professor Suzanne Scarlata – Dr. Nima Rahbar | How a Biological Enzyme Could Help Concrete to Heal Itself
As an inherently brittle material, concrete often needs to be replaced after just a few decades: driving a demand which incurs significant costs for Earth’s climate. Through their research, Professors Suzanne Scarlata and Nima Rahbar at Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Massachusetts, introduce a new mechanism that allows concrete to quickly repair itself, with the help of an enzyme vital to the function of living cells. This approach could help to reduce the world’s insatiable demand for concrete.
Dr Di Yun | Lessons from Tai-Chi could make Travelling Wave Reactors a reality
In principle, travelling wave reactors offer a safe, highly efficient approach to generating nuclear power. However, development has been held back by a variety of challenges linked to the need for extensively high burn-up in the reactor core, meaning very high rates of generated energy which can damage the reactor. Inspired by the principles of Tai-Chi, a team led by Di Yun from Xi’an Jiaotong University has shown that with the right approach, a high temperature operation, usually deemed as a threat, can be transformed into useful advantages, bringing the practical rollout of travelling wave reactors one step closer to reality.
Dr Li Lu | An illusion of parallax: explaining a mysterious signal at the edge of the solar system
In 2009, astronomers detected a mysterious source of high-energy, chargeless particles, which appeared to originate from the very edge of the solar system. Through fresh analysis, Dr Li Lu and colleagues at the Chinese Academy of Sciences have discovered that this distance may be an illusion, created by an effect relating to the solar wind as viewed by the commonly used parallax method. If correct, the team’s theory suggests that the as-yet enigmatic signal could actually originate from a source just beyond Earth’s atmosphere.