The Shape of Rational Choices in Game Theory – Dr Tarun Sabarwal, University of Kansas
Original Article Reference
https://doi.org/10.26320/SCIENTIA212
Share Episode
About this episode
The choices we make in various situations have collective effects on the patterns of overall movement in conflict and cooperation. Dr Tarun Sabarwal at the University of Kansas is investigating the ways in which the overall pictures produced by these behaviours can be predicted through mathematical models of game theory.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. 
What does this mean?
Share: You can copy and redistribute the material in any medium
or format
Adapt: You can change, and build upon the material for any
purpose, even commercially.
Credit: You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the
license, and indicate if changes were made.
Related episodes
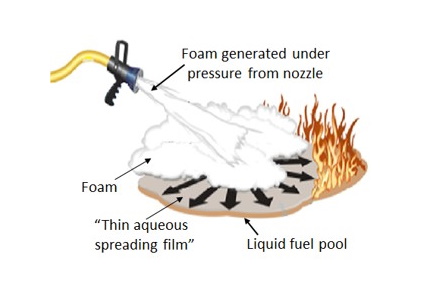
Dr. Arthur Snow | From Firefighting Foams to Molecular Mysteries: A Surfactant’s Unexpected Journey
Scientific discovery often unfolds in unexpected ways. What begins as a search for solutions to real-world challenges can lead researchers into unexplored scientific territory, where unconventional ideas emerge and spark debate. This dynamic was at the heart of research by Dr. Arthur W. Snow and Dr. Ramagopal Ananth in the Chemistry Division of the US Naval Research Laboratory. Their study aimed to address a pressing need: replacing fluorocarbon surfactants in firefighting foams. What they discovered would take them beyond firefighting applications and into fundamental questions about the nature of water itself.
Dr. Angel Ford – Dr. Daniel Alemneh | Amplifying Global Voices: The Fight for Fairness in Scholarly Communication
In our increasingly interconnected world, sharing knowledge freely and fairly is crucial for ongoing development and progress. Increasing the overall size of our store of knowledge is important in dealing with the challenges we face in the modern world, but determining who can access and add to that knowledge is a key question. Prestigious academic journals and global conferences aim to help disseminate our most important discoveries and innovations, but researchers do not have equal access to such resources to promote their ideas and consequently not all voices are heard equally. Scholars from low- and middle-income countries continue to face invisible walls that limit their participation in the global exchange of ideas. This systemic imbalance is the focus of a deeply insightful study by Dr. Angel Ford of the University at Albany and Dr. Daniel Alemneh of the University of North Texas, who call for a more just and healthier scholarly communication system.
Dr Aikaterini-Christina Koula | How the law is used to silence Human Rights Defenders
Research from Dr Aikaterini-Christina Koula at Manchester Metropolitan University reveals how legal systems are increasingly being weaponized to silence human rights defenders, particularly in Europe. Her work introduces a taxonomy of violations perpetrated through the legal system and demonstrates how these tactics deviate from human rights standards, offering valuable insights for academics, practitioners, and defenders alike.
Professor Germaine A. Hoston | How Traditional Chinese Philosophy Shaped Modern Revolutionary Thought
Research from Professor Germaine A. Hoston at the University of California, San Diego, reveals how traditional Chinese philosophical idealism influenced the development of Chinese Marxism. Her findings demonstrate that despite their rejection of China’s feudal past, key Chinese Marxist theorists like Li Dazhao and Mao Zedong incorporated elements of Neo-Confucian idealism into their revolutionary philosophy. This “sinification” of Marxism drew particularly on concepts of consciousness, will, and the unity of knowledge and action from traditional Chinese thought, creating a uniquely Chinese revolutionary philosophy that challenged Soviet economic determinism.
Increase the impact of your research
• Good science communication encourages everyday people to be scientifically literate so that they can analyse the integrity and legitimacy of information.
• Good science communication encourages people into STEM-related fields of study and employment.
• Good public science communication fosters a community around research that includes both members of the public, policymakers and scientists.
• In a recent survey, 75% of people suggested they would prefer to listen to an interesting story than read it.

Upload your science paper
Step 2
SciPod script written
Step 3
Voice audio recorded
Step 4
SciPod published