Simulating Supersonic Fluid Flows in the Student Aerodynamics Lab – Dr Oleg Goushcha, Manhattan College
Original Article Reference
This SciPod is a summary of the papers ‘Revival of water table experiments in fluid mechanics courses, part I’ and ‘Revival of water table experiment in fluid mechanics courses, part II’, from the International Journal of Mechanical Engineering Education. https://doi.org/10.1177/0306419019831393
Share Episode
About this episode
When learning about fluid dynamics, physics and engineering students can benefit greatly from hands-on experiments that allow them to visualise the equations they learn in lectures. For supersonic flows, however, the equipment required is incredibly expensive, making some experiments inaccessible to many universities. Dr Oleg Goushcha at Manhattan College has revived an old methodology to demonstrate supersonic flows in the classroom using far more affordable equipment. He has shown that the features seen in supersonic can be accurately simulated through an inexpensive setup involving water surface waves.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. 
What does this mean?
Share: You can copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
Adapt: You can change, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
Credit: You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made.
Related episodes
Dr. Sarah Hallen | The patient will see you all now: redesigning clinical learning for better outcomes
If you picture doctors making their daily rounds through hospital floors, you might imagine a single doctor standing by a bedside, examining a patient’s chart, or perhaps a group of doctors discussing a case right outside a patient’s room. However, the future of hospital care may well look more like a well-choreographed team effort, with doctors, nurses, pharmacists, students, and patients themselves, all in the same room, and all working as one team. This is exactly what Dr. Sarah Hallen and her colleagues at MaineHealth Maine Medical Center Portland envisioned when they created the iPACE model, short for Interprofessional Partnership to Advance Care and Education. Launched in 2017, this model is not just changing how doctors are trained; it’s leveraging team synergies to reshape what it means to deliver healthcare.
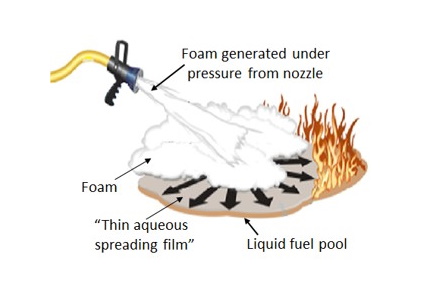
Dr. Arthur Snow | From Firefighting Foams to Molecular Mysteries: A Surfactant’s Unexpected Journey
Scientific discovery often unfolds in unexpected ways. What begins as a search for solutions to real-world challenges can lead researchers into unexplored scientific territory, where unconventional ideas emerge and spark debate. This dynamic was at the heart of research by Dr. Arthur W. Snow and Dr. Ramagopal Ananth in the Chemistry Division of the US Naval Research Laboratory. Their study aimed to address a pressing need: replacing fluorocarbon surfactants in firefighting foams. What they discovered would take them beyond firefighting applications and into fundamental questions about the nature of water itself.
Dr. Jon Reinders | A genetic breakthrough for farming: editing corn inside the plant, not the lab
Corn is a cornerstone of modern agricultural food production, particularly in North America. Humans have selectively bred such crops over generations to create better yields, improved appearance and flavor and enhanced disease resistance. However, what if we could skip these arduous rounds of selective breeding and improve a crop’s stability and reliability regardless? Deep within the genetic blueprint of every maize kernel, scientists are aiming to achieve just this. In a recent groundbreaking study, Dr. Jon Reinders of Corteva Agriscience and his colleagues have unveiled a powerful new way to create genetically improved corn, not in a lab dish, but inside the plant itself. This new method is faster, cleaner, safer, and could transform how we grow our most essential crops.
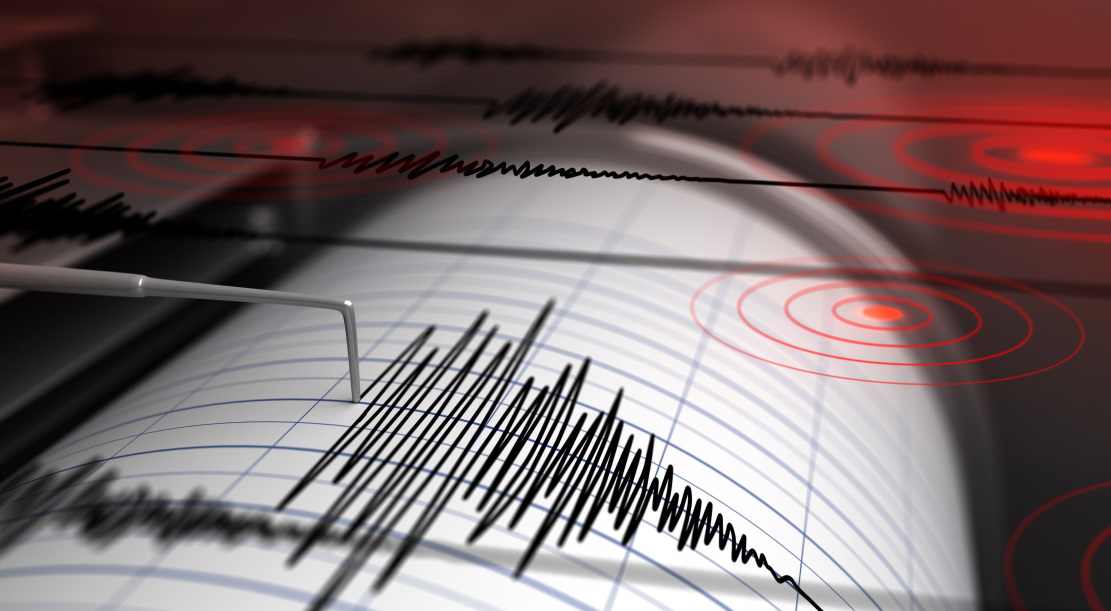
Professor Jeremy Maurer | Building a seismic timeline of the Nippes earthquake
Sitting directly over a complex network of fault lines, Haiti is one of the most earthquake-prone nations on Earth. In 2021, the Nippes earthquake became the latest to devastate the country, and today, researchers are still piecing together the timeline of seismic events which unfolded during the earthquake. Through their research, Professor Jeremy Maurer and colleagues at Missouri University of Science and Technology have described how the Nippes earthquake originated, shifted, and ruptured a major fault line, triggering numerous ‘afterslip’ events in the following days.
Increase the impact of your research
• Good science communication encourages everyday people to be scientifically literate so that they can analyse the integrity and legitimacy of information.
• Good science communication encourages people into STEM-related fields of study and employment.
• Good public science communication fosters a community around research that includes both members of the public, policymakers and scientists.
• In a recent survey, 75% of people suggested they would prefer to listen to an interesting story than read it.

Step 1 Upload your science paper
Step 2 SciPod script written
Step 3 Voice audio recorded
Step 4 SciPod published