Harnessing Water Fleas to Purify Wastewater
Original Article Reference
This SciPod is a summary of the information held in patent document ‘Using Daphnia for bioremediation’. Patent Information: WO/2021/116229.
About this episode
Water-treatment processes are essential for water reuse in municipal, agricultural and industrial applications. Wastewater treatment ensures our safety and prevents sickness and death from parasites and contaminants every year. However, certain chemical contaminants, such as pharmaceuticals and pesticides, are difficult to remove from water, and can accumulate in the food web, eventually entering our food supply and potentially causing adverse health outcomes. Dr Luisa Orsini [Loo-ee-sah Oar-see-nee] and her colleagues at Daphne Water Solutions Ltd have developed a cutting-edge water-bioremediation technology, which is based on the use of small aquatic invertebrates called water fleas. By removing harmful contaminants from water, the sustainable and eco-friendly technology enables water reuse, while protecting human health and the environment.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. 
What does this mean?
Share: You can copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
Adapt: You can change, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
Credit: You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made.
More episodes
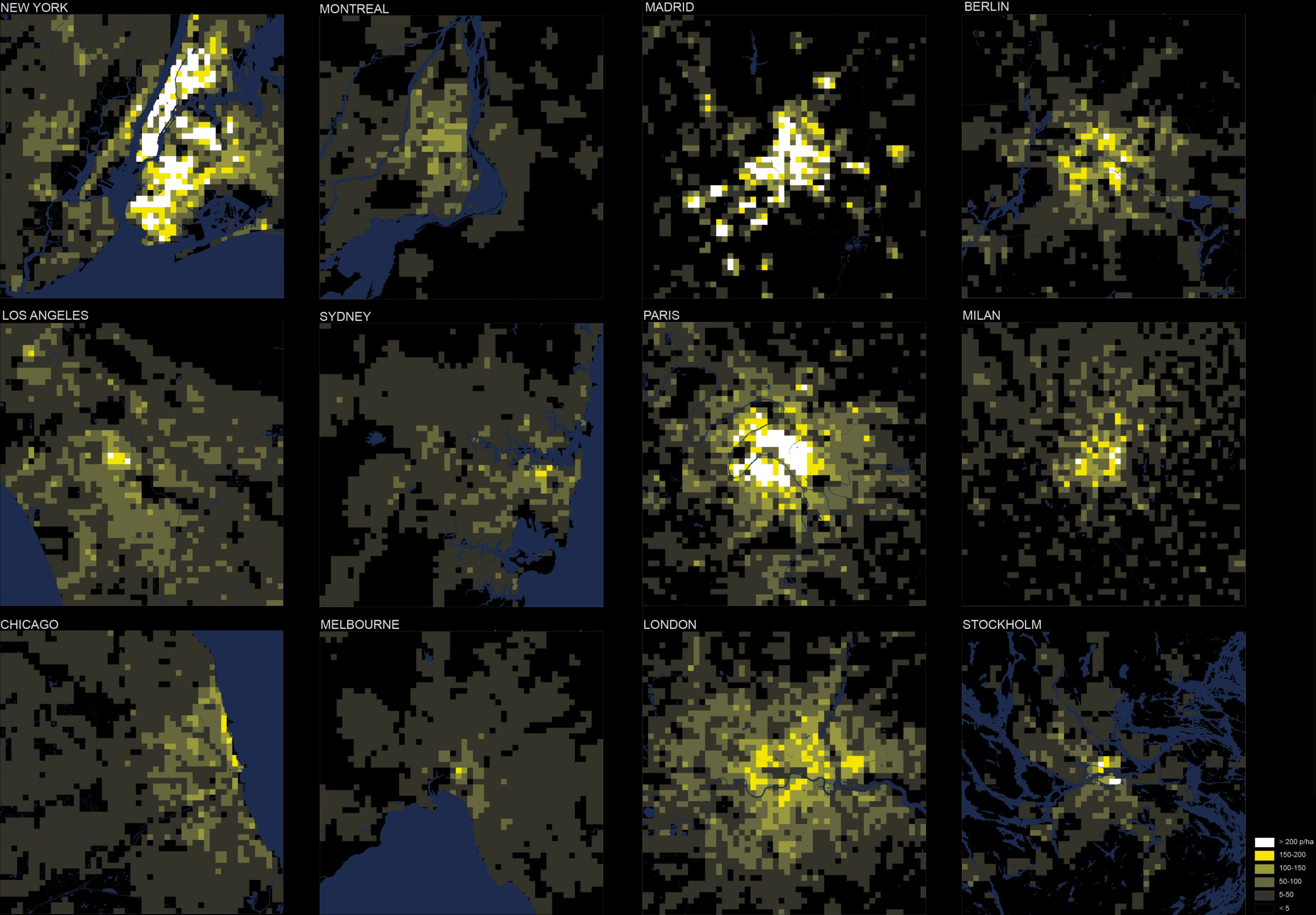
Dr Elek Pafka | Mapping urban density from the neighbourhood to the metropolis
So far, approaches to mapping the density of cities have often been oversimplified, causing them to overlook many key aspects of everyday urban life. Through his research, Dr Elek Pafka at the University of Melbourne introduces two new metrics for measuring urban density, which better capture its complex, multi-scale variations. His research offers deeper insights into how people experience and interact with cities, and could lead to new strategies to make our cities more productive, sustainable, and better places to live.
Dr Di Yun | Lessons from Tai-Chi could make Travelling Wave Reactors a reality
In principle, travelling wave reactors offer a safe, highly efficient approach to generating nuclear power. However, development has been held back by a variety of challenges linked to the need for extensively high burn-up in the reactor core, meaning very high rates of generated energy which can damage the reactor. Inspired by the principles of Tai-Chi, a team led by Di Yun from Xi’an Jiaotong University has shown that with the right approach, a high temperature operation, usually deemed as a threat, can be transformed into useful advantages, bringing the practical rollout of travelling wave reactors one step closer to reality.
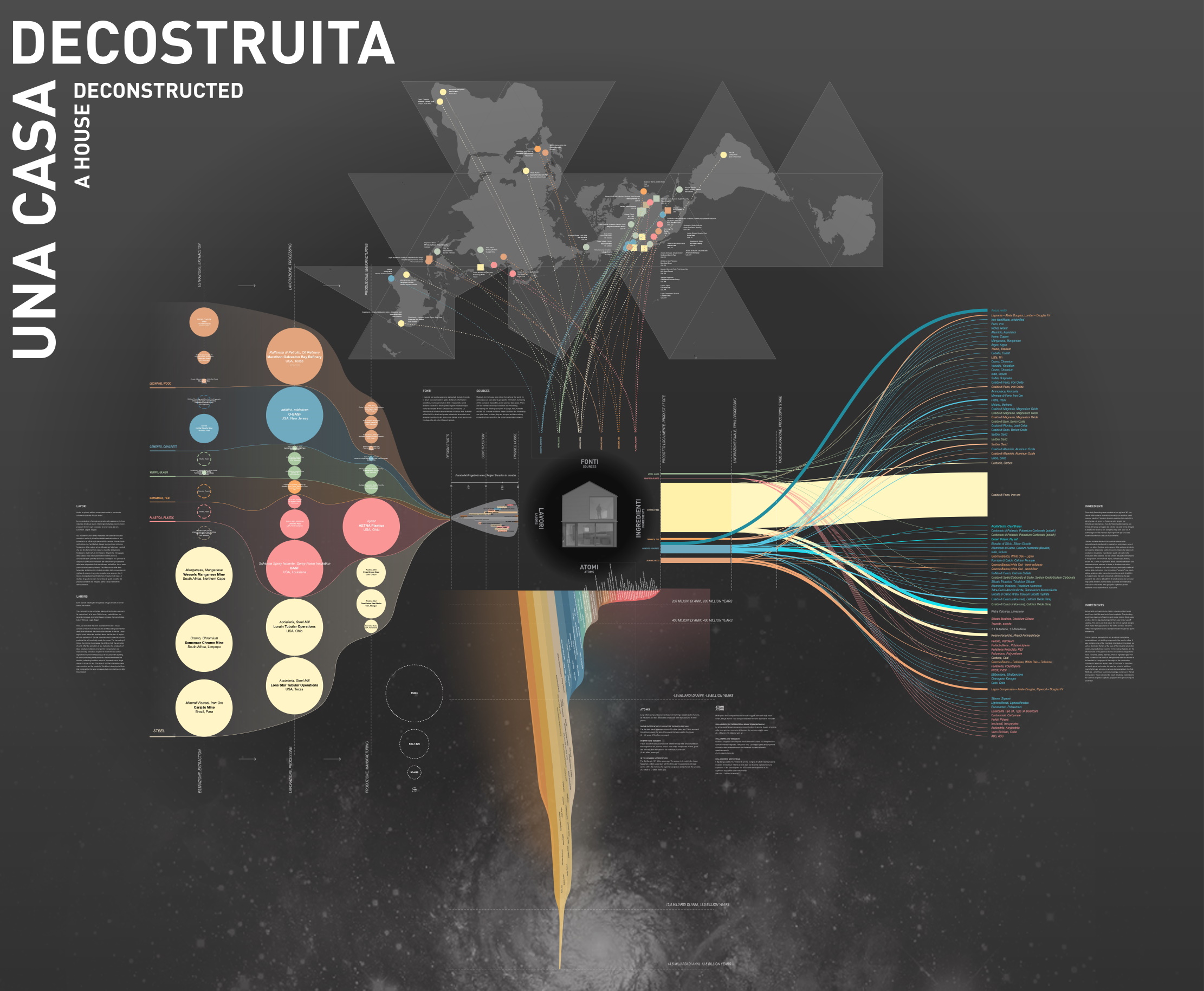
Professor Mark Jarzombek | A House Deconstructed: Uncovering the Hidden History of the Modern House
The full extent of the labour and resources which go into creating a modern house is hidden deeply within the buildings we call home. Professor Mark Jarzombek of MIT and Professor Vikramaditya Prakash of the University of Washington are co-founders of the Office of Uncertainty Research, a research collaboration that is dedicated to rethinking architecture in a modern context. Through their research, Jarzombek and Prakash investigate these hidden stories by exploring the history of a recently built modern house in Seattle. Their findings reveal that the presumed transparency of modern architecture conceals deep ethical and environmental challenges, inspiring a call for a critical reassessment of how our current construction practices should be understood and approached.
Prof. Andisheh Dadashi | Unraveling the Mysteries of Human Embryo Metabolism: Insights from Computational Models
Metabolism is the cornerstone of life, orchestrating the myriad chemical reactions that sustain cells, tissues, and organisms. It drives growth, division, energy production, and cellular maintenance. For scientists, understanding metabolism, particularly during the earliest stages of human development, holds the key to uncovering the origins of various diseases and developmental disorders. However, studying metabolism in human embryos presents formidable challenges due to ethical considerations, their tiny size, and the intricate web of metabolic pathways. In a groundbreaking study, researchers Prof. Andisheh Dadashi and Derek Martinez of the University of New Mexico-Valencia leveraged advanced computational models to shed light on the metabolic processes occurring in human embryos during the critical peri-implantation stage.
Increase the impact of your research
• Good science communication helps people make informed decisions and motivates them to take appropriate and affirmative action.
• Good science communication encourages everyday people to be scientifically literate so that they can analyse the integrity and legitimacy of information.
• Good science communication encourages people into STEM-related fields of study and employment.
• Good public science communication fosters a community around research that includes both members of the public, policymakers and scientists.
• In a recent survey, 75% of people suggested they would prefer to listen to an interesting story than read it.

Step 1 Upload your science paper
Step 2 SciPod script written
Step 3 Voice audio recorded
Step 4 SciPod published