Frozen in Time: The Permafrost Microbiome – Professor Rachel Mackelprang, California State University, Northridge
May 14, 2018biology, earth and environment
Deep within the permafrost, viable microbial communities persist, buried for millennia. With the permafrost rapidly thawing due to global warming, these microbes are becoming more active, feeding on previously frozen organic matter and ‘breathing’ out greenhouse gases, further exacerbating climate change. Professor Rachel Mackelprang of California State University is studying the significance of these little-understood microbes. Funded by NASA, her team is also investigating how these hardy microbes adapt and survive as an analogue of how extra-terrestrial life may survive in sub-zero space environments.

You may also like …
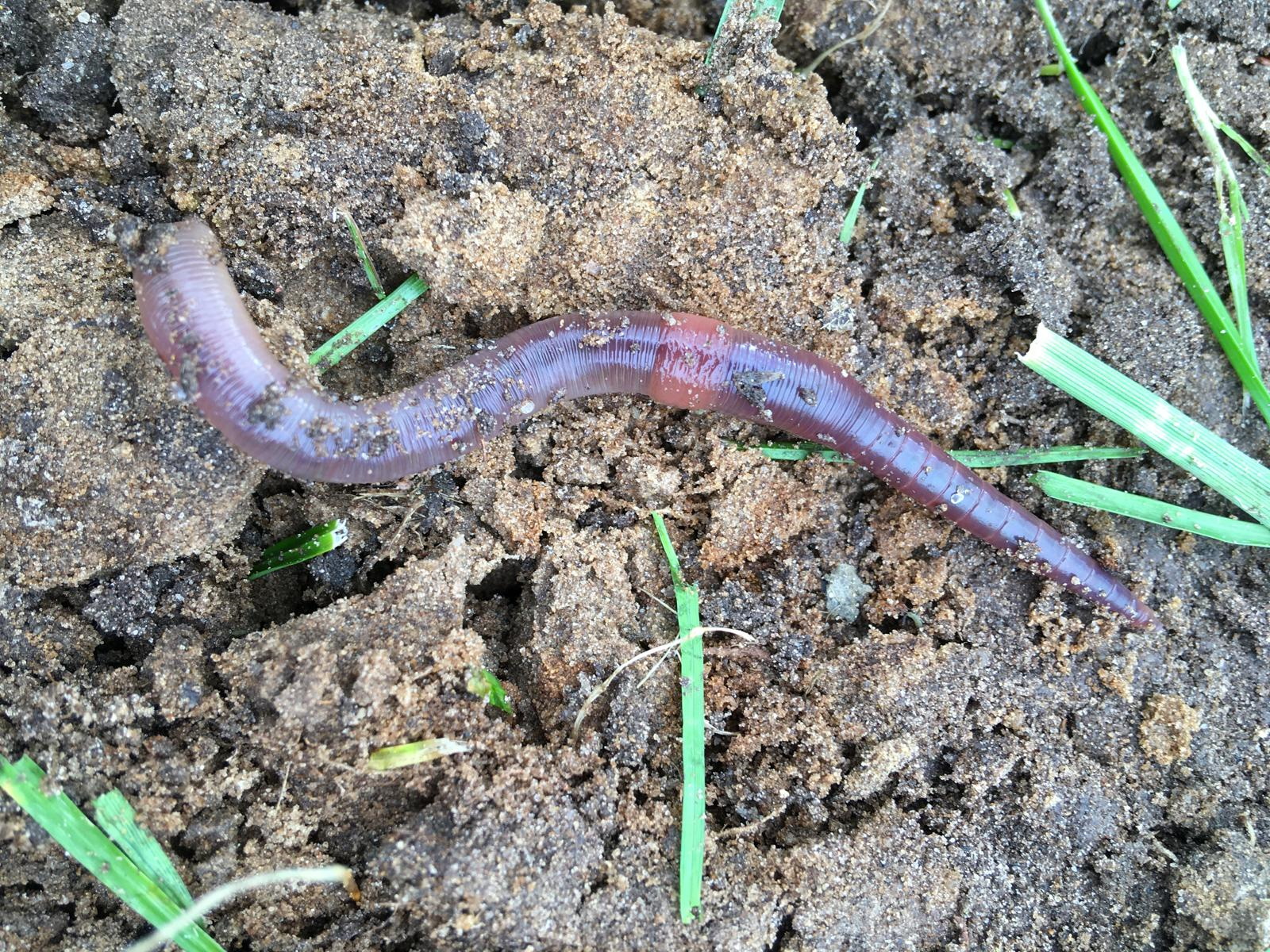

Roos van de Logt | Hidden Engineers: How Earthworms Could Help Us Weather a Changing Climate
If you were to observe a quiet Dutch pasture, you might not guess that one of the most important climate-resilience workers in the landscape is silently engineering the soil beneath the grass. However, just below your feet, an unassuming creature plays a role in buffering floods, preserving crops during droughts, and quietly maintaining the natural plumbing system of the land. This creature is the humble deep-burrowing earthworm, Lumbricus terrestris (or L. terrestris for short). In recent years, researcher Roos van de Logt of the Louis Bolk Institute, and colleagues, have been uncovering the surprisingly complex story of this earthworm. Their findings suggest that supporting, and in some cases reintroducing, L. terrestris could be a powerful, nature-based tool for helping European grasslands adapt to intensifying climate extremes.
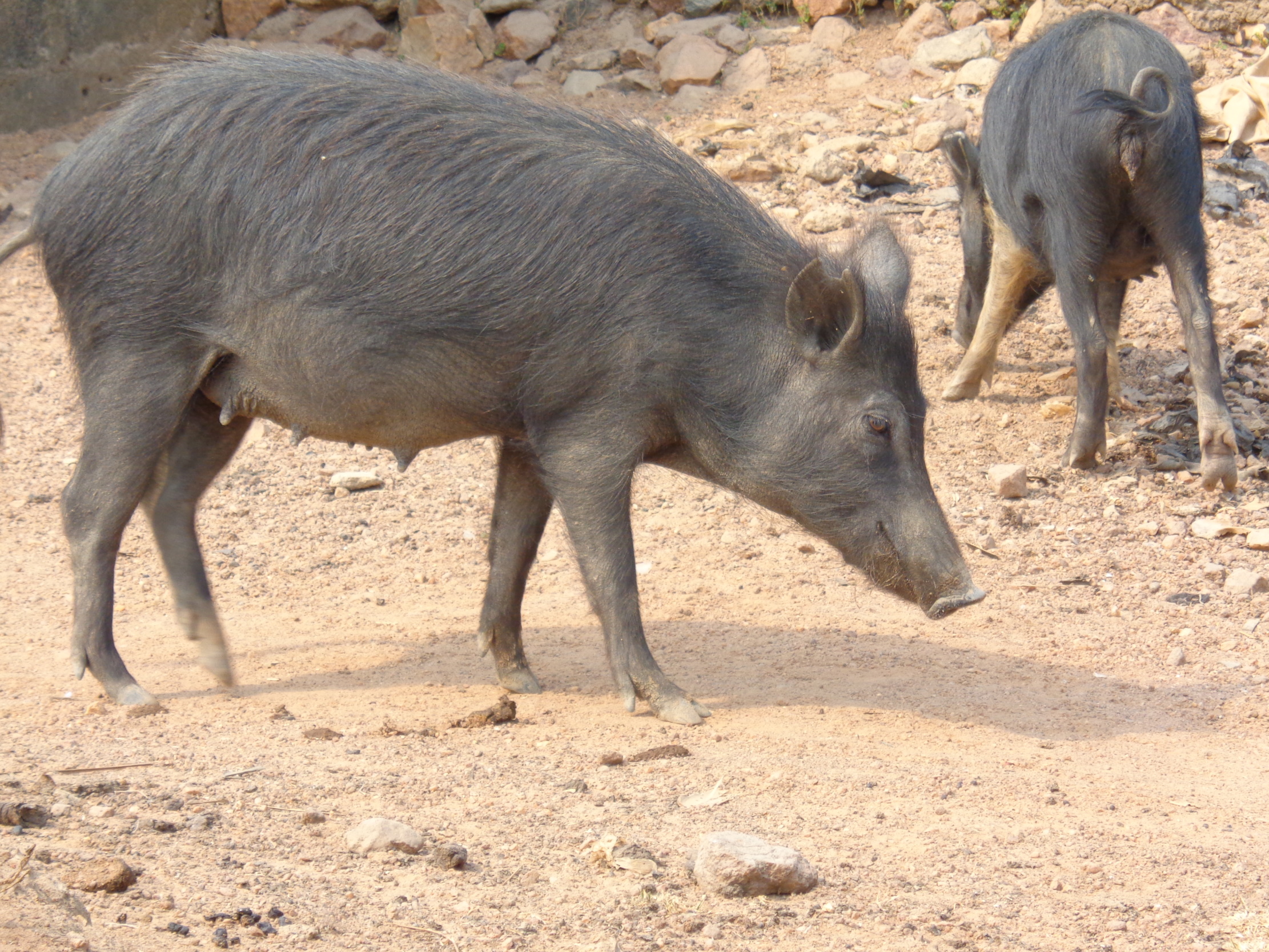

Associate Professor Adeniyi Charles Adeola | History Written in Base-Pairs: The Hidden Stories in African Pig Genomes
Africa is often described as a continent of extremes. Vast deserts give way to lush rainforests; humid coastlines sit beside high, cool plateaus; ancient savannas stretch for thousands of kilometers. Life in Africa has always existed at the edge of change, shaped by heat and drought, abundance and scarcity. Survival here has never been guaranteed, it has had to be earned, generation by generation, through adaptation. Nowhere is this long story of adjustment and resilience written more clearly than in DNA.
Dr. Jürgen Gailer | Linking the Blood Chemistry of Metals with Adverse Human Health: New Tools Reveal an Invisible World
Researchers Maryam Doroudian and Jürgen Gailer from the University of Calgary explore what happens when red blood cells rupture and release a zinc-containing enzyme called carbonic anhydrase 1 into the bloodstream, revealing that it remains unexpectedly free and may influence vascular health. Their work also connects to broader research showing how liquid chromatography is transforming our ability to study toxic cadmium and mercury as they move through the body. Together, these studies uncover hidden biochemical processes that shape how environmental pollutants and blood-cell damage affect human health.
Dr. Reginald O’Hara | Regulating Resilience: Caffeine, Neuromodulation, and the Biology of Performance
In an era defined by constant pressure, chronic stress, and escalating performance demands, the question of how humans sustain physical and mental effectiveness has never been more urgent. From soldiers operating under sleep deprivation and extreme physical strain to civilians navigating relentless workloads and psychological stress, fatigue has become the defining challenge of modern life. However, fatigue is not simply a matter of willpower or motivation; it is a complex biological signal arising from the interaction of muscles, metabolism, the brain, and the autonomic nervous system. Recent research, including work led and coauthored by Dr. Reginald O’Hara, Director of the Applied Health and Performance Division at Sophic Synergistics in Houston Texas, and former Director of the Military Performance Laboratory at Brooke Army Medical Center and the Air Force Research Laboratory, offers a more sophisticated understanding of how performance can be preserved, without pushing the human body beyond its safe limits.

Dr. Kai Hilpert | AI-Powered Prediction of Antimicrobial Peptides in Human Serum: A New Strategy Against Resistant Bacteria
In the 20th century, antibiotics transformed medicine. Infections that once killed millions could be cured with a pill or injection. Surgeries became safer, cancer treatments more effective, and advanced medical interventions, such as organ transplants, became possible, all because doctors could rely on these drugs to control infections. Unfortunately, today, that foundation is crumbling. Bacteria are evolving faster than medicine can keep up. Common antibiotics are failing, and infections that were once easily treatable are becoming deadly again. In 2019 alone, antimicrobial resistance was linked to nearly five million deaths worldwide, making it deadlier than HIV or malaria. The economic cost is equally staggering: the World Bank warns of trillions lost in global productivity and millions pushed into poverty if nothing changes. This crisis, caused by antimicrobial resistance, has been described as a “silent pandemic.” Unlike a sudden outbreak, it spreads quietly, making routine medical care slightly more dangerous each year. Yet amid this grim outlook, new research is opening a window of hope. At the forefront of new innovations in this area are Dr. Kai Hilpert of City St George’s, University of London, and his colleagues, who are pioneering an approach that combines biology, chemistry, and artificial intelligence to reinvent how we discover infection-fighting medicines. Their work has been recognised with a prestigious award from the UK’s Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, BBSRC.
Dr. Jacqueline Tabler | The Self-Organizing Bone Wave Underlying Skull Growth
We typically take our skulls for granted, beyond their basic function in keeping our brain safe and sound within our head. When you look in the mirror, the shape of your skull, which forms the very structure beneath your face, is something you may not have considered in much detail. However, the story of how your skull came to be, and how bone spread across your embryonic head in perfect symmetry to form a complete and protective dome over your brain, is a marvel of biology that scientists are only just beginning to understand. In a new study led by Dr. Jacqueline Tabler at the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics, researchers have uncovered a surprising and elegant mechanism behind how skull bones grow that is different to how we typically think of cell movement and migration in the body. Published in the open-access journal Nature Communications, this latest research rewrites what we thought we knew about cell movement, tissue development, and the mechanics of morphogenesis, the process through which an organism takes shape.

Dr Malgorzata Trela – Dr Sophie Rutschmann | From Classroom to Conference: How a New Teaching Model Lets Students Step Inside the Scientific Community
When you imagine a scientific conference, you may picture rows of poster boards, bustling coffee breaks, and seasoned researchers discussing the latest data and research approaches. It can feel like a world reserved for insiders. Yet a recent study led by Dr Malgorzata Trela and Dr Sophie Rutschmann at Imperial College London argues that this lively professional gathering is precisely where tomorrow’s scientists ought to cut their teeth. Their paper, “Immunology in Practice: a modular framework to support Master of Science students’ conference attendance and engagement,” describes an educational project that turns a four-day professional congress into the beating heart of a master’s-level module, and in doing so, reshapes how students learn, network and even see themselves.
Ren Kimura | Listening to Our Cats’ Kidneys: How a Handful of Mirror-Image Molecules Could Reveal Feline Health
Amino acids are a fundamental building block for fur, muscle, and every other living tissue on Earth. These molecules come in “left-handed” (L) and “right-handed” (D) forms, a bit like gloves that fit different hands or mirror images. Life largely runs on the left-handed set, so biologists once assumed the right-handed versions were irrelevant. Yet nature quietly manufactures these D-amino acids and they can play a role in certain biological processes. In research led by Japanese analytical chemist Ren Kimura of the R&D-Analytical Science Research department of the Kao Corporation, Japan, researchers reveal that these overlooked molecules may offer an early-warning beacon for one of the most common and deadly ailments in cats, chronic kidney disease (or CKD for short), and they may even have potential in diagnosing human conditions.

Dr. Jon Reinders | A genetic breakthrough for farming: editing corn inside the plant, not the lab
Corn is a cornerstone of modern agricultural food production, particularly in North America. Humans have selectively bred such crops over generations to create better yields, improved appearance and flavor and enhanced disease resistance. However, what if we could skip these arduous rounds of selective breeding and improve a crop’s stability and reliability regardless? Deep within the genetic blueprint of every maize kernel, scientists are aiming to achieve just this. In a recent groundbreaking study, Dr. Jon Reinders of Corteva Agriscience and his colleagues have unveiled a powerful new way to create genetically improved corn, not in a lab dish, but inside the plant itself. This new method is faster, cleaner, safer, and could transform how we grow our most essential crops.

Prof. Nelson Gekara | The Guardians of the Gut: A New Frontier in the Defence Against Viruses
Our gut contains a sleepless army, creating a hostile environment for pathogens, and helping to fortify our body’s immune defences. It may surprise you to learn that this army isn’t even human in nature, but is bacterial. The trillions of bacteria that naturally live in our gut, known as the gut microbiota, form an important component of our overall immunity against infectious disease. While bacteria can also cause disease, beneficial bacteria naturally colonise available spaces in our body, such as the gut, and play a key role in our immunity and physiology. Research conducted by Prof. Nelson Gekara of Stockholm University in Sweden and colleagues has revealed that these microscopic organisms play a crucial role in protecting us from viral infections, even in organs that are unconnected to the gut. Their study, published in the journal Immunity, uncovers a fascinating link between the gut microbiota and our body’s ability to fight viruses, offering new insights into immune function and the unintended consequences of antibiotic use.