Identifying an Achilles’ Heel in Insecticide Resistance – Dr Barry Pittendrigh, Purdue University
Original Article Reference
This SciPod is a summary of the paper ‘The insulin signalling pathway in Drosophila melanogaster. A nexus revealing an “Achilles’ heel” in DDT resistance’, published in Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology. doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2020.104727
About this episode
Insecticide resistance is an ongoing challenge for agriculture and the control of insect-transmitted diseases. In a recent study at Purdue University, a team of scientists led by Dr Barry Pittendrigh identified a potential chink in the armour of insecticide resistance in fruit flies. If this Achilles’ heel can be exploited, it bodes well for the future control of destructive insects.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. 
What does this mean?
Share: You can copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
Adapt: You can change, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
Credit: You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made.
More episodes
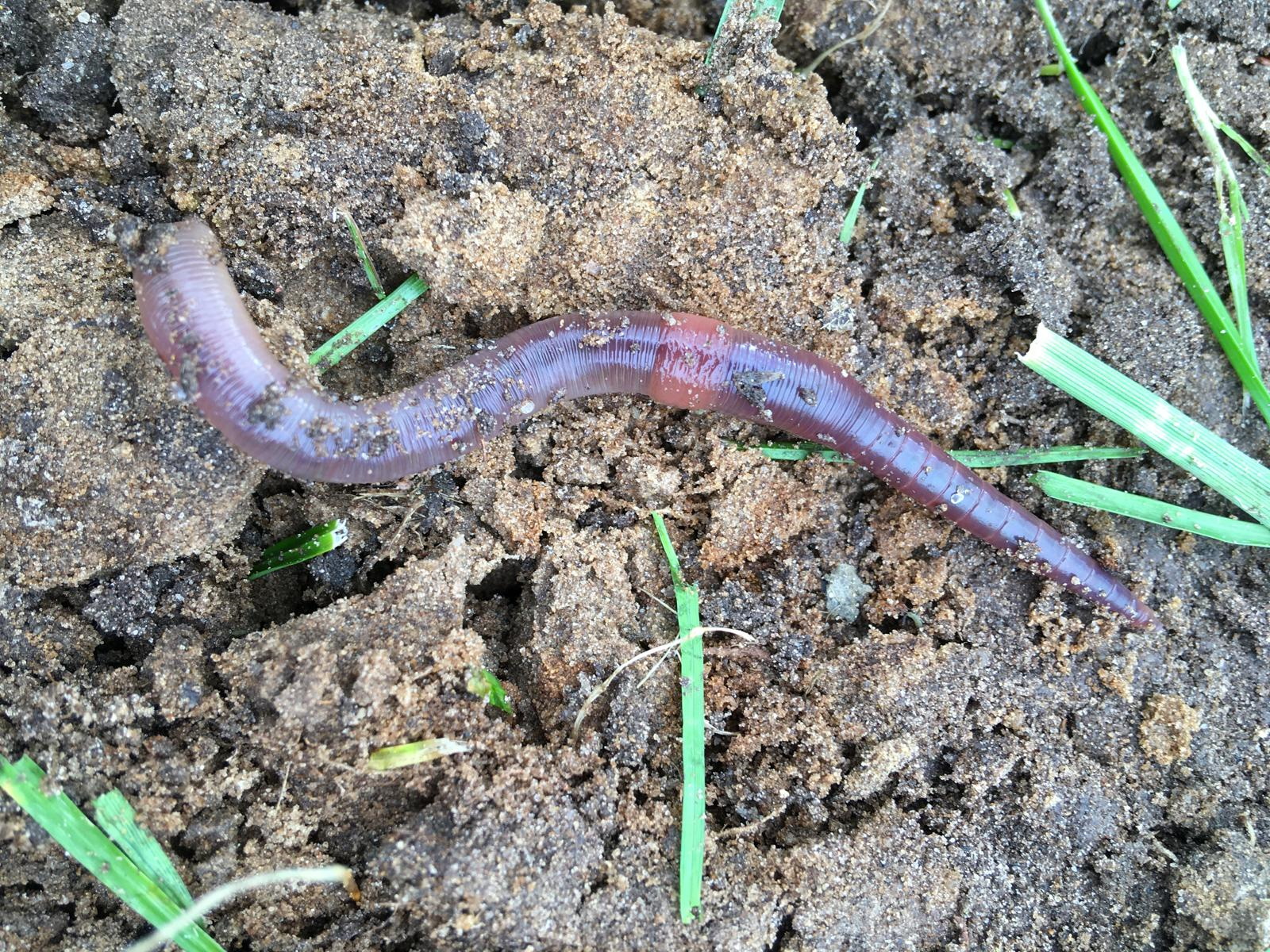
Roos van de Logt | Hidden Engineers: How Earthworms Could Help Us Weather a Changing Climate
If you were to observe a quiet Dutch pasture, you might not guess that one of the most important climate-resilience workers in the landscape is silently engineering the soil beneath the grass. However, just below your feet, an unassuming creature plays a role in buffering floods, preserving crops during droughts, and quietly maintaining the natural plumbing system of the land. This creature is the humble deep-burrowing earthworm, Lumbricus terrestris (or L. terrestris for short). In recent years, researcher Roos van de Logt of the Louis Bolk Institute, and colleagues, have been uncovering the surprisingly complex story of this earthworm. Their findings suggest that supporting, and in some cases reintroducing, L. terrestris could be a powerful, nature-based tool for helping European grasslands adapt to intensifying climate extremes.
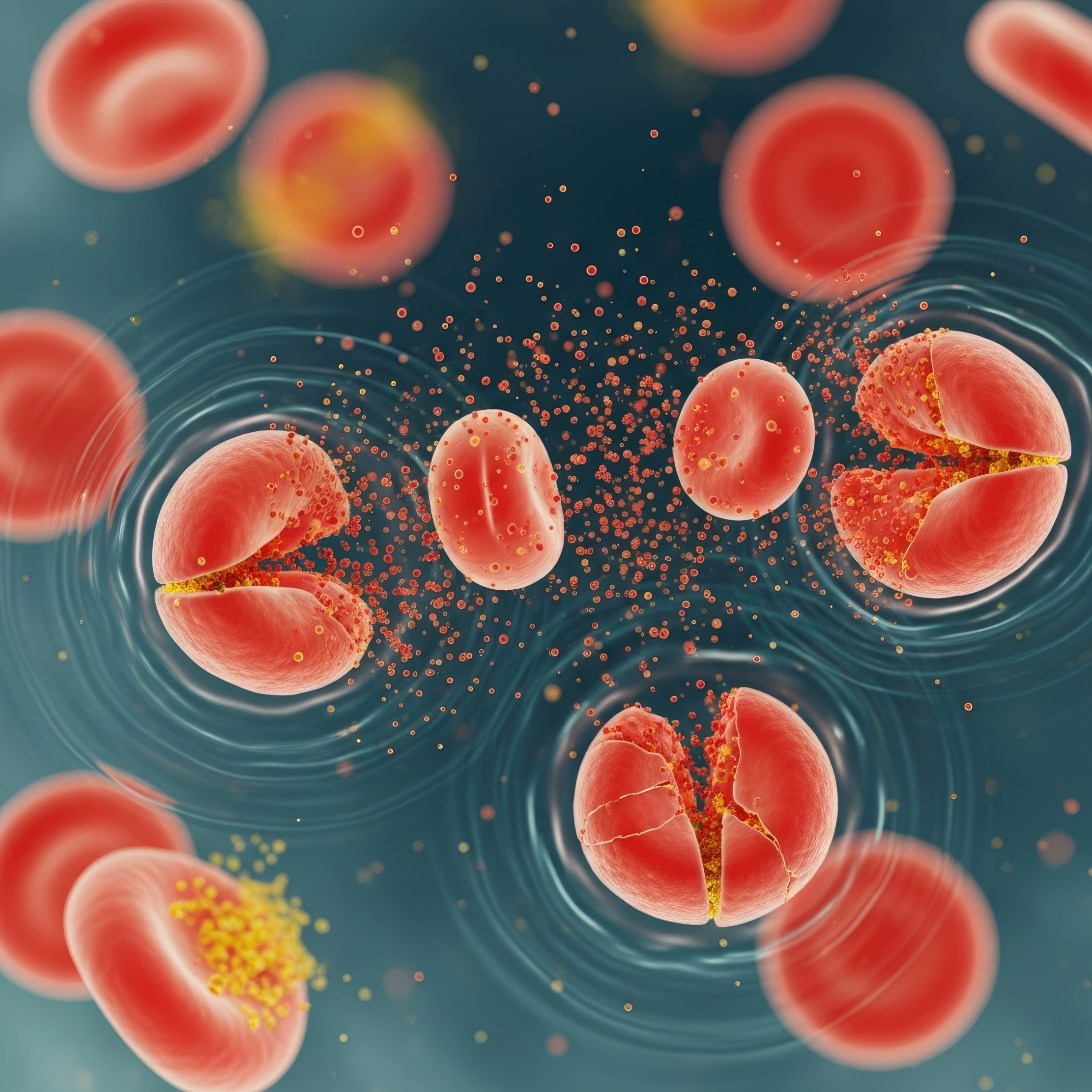
Dr. Jürgen Gailer | Linking the Blood Chemistry of Metals with Adverse Human Health: New Tools Reveal an Invisible World
Researchers Maryam Doroudian and Jürgen Gailer from the University of Calgary explore what happens when red blood cells rupture and release a zinc-containing enzyme called carbonic anhydrase 1 into the bloodstream, revealing that it remains unexpectedly free and may influence vascular health. Their work also connects to broader research showing how liquid chromatography is transforming our ability to study toxic cadmium and mercury as they move through the body. Together, these studies uncover hidden biochemical processes that shape how environmental pollutants and blood-cell damage affect human health.
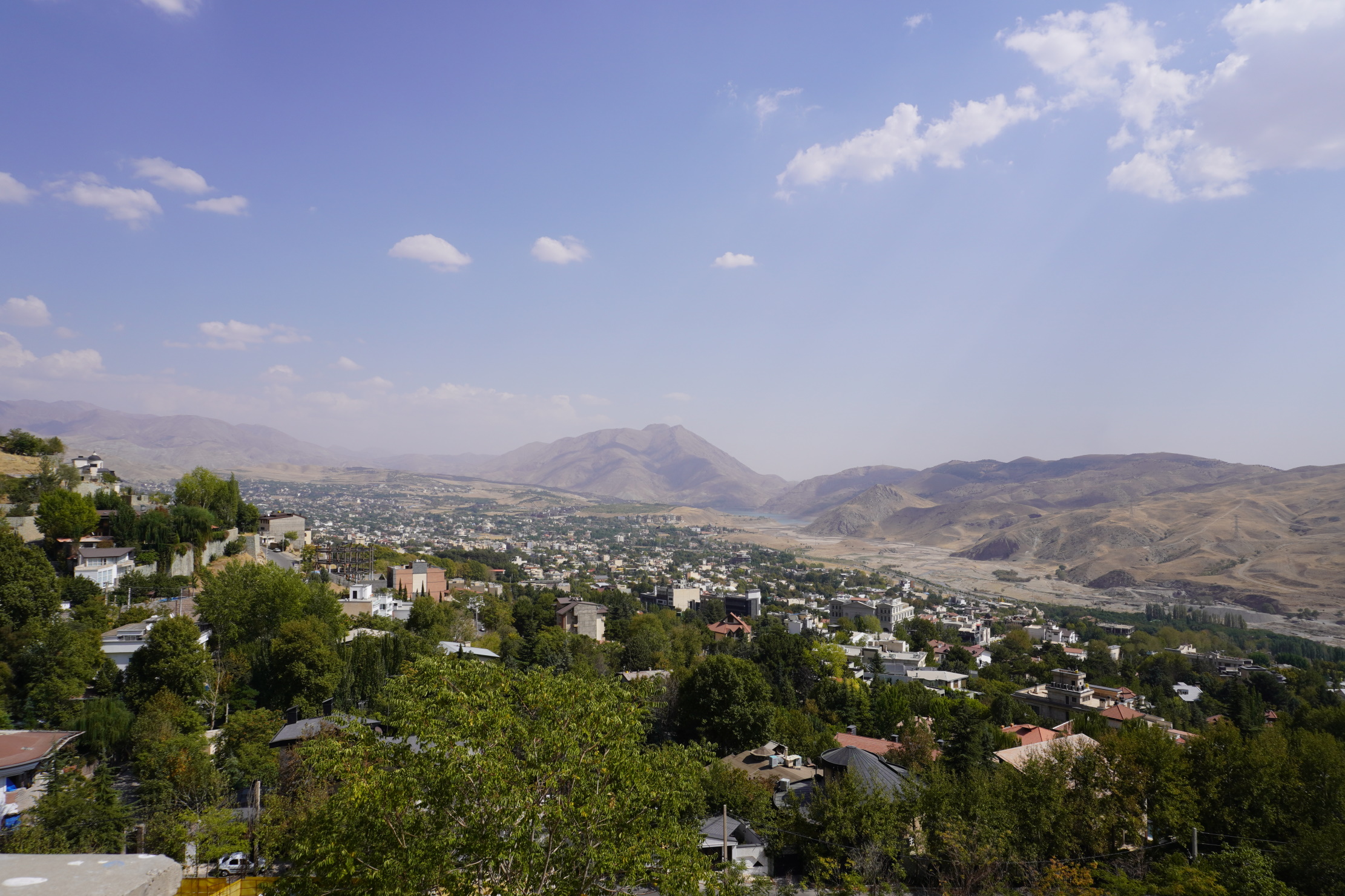
Prof. Satoshi Abe | The Unexpected Symbols Driving Iran’s Environmental Movement
If you walk through the bustling streets of Tehran, you might first notice the traffic, the densely packed apartments, or young people weaving through the city on motorbikes. But if you look a little closer, you may notice banners stretching across overpasses, tiny flags lining the perimeters of parks, or posters taped to walls, and you might just begin to sense something else humming quietly in the background: a story about nature, identity, and the nation itself. According to Prof. Satoshi Abe of Tottori University, Japan, who has researched environmental activism in Iran, the country is experiencing not just an environmental crisis, but an environmental reimagining. Iranians are not simply debating water shortages, air pollution, or endangered species, though they are certainly doing that. They are also wrestling with questions about what “nature” means within the story of Iran.
Easing the Hardest Moment: How Brain Stimulation Is Transforming Care for People with Opioid Use Disorder
In the world of opioid addiction treatment, the hardest moment often arrives precisely when hope begins to emerge. It is the moment someone chooses to stop using opioids. That decision, courageous and life-changing, almost immediately collides with one of the most punishing physiologic syndromes known in medicine: opioid withdrawal. Withdrawal brings waves of nausea, sweats, shaking, cramps, insomnia, anxiety, and extremely intense cravings. For countless individuals, this moment is a seemingly inescapable stumbling block that can be the undoing of their recovery. They want to stop, they mean to stop, but withdrawal can become an insurmountable barrier.
Increase the impact of your research
• Good science communication helps people make informed decisions and motivates them to take appropriate and affirmative action.
• Good science communication encourages everyday people to be scientifically literate so that they can analyse the integrity and legitimacy of information.
• Good science communication encourages people into STEM-related fields of study and employment.
• Good public science communication fosters a community around research that includes both members of the public, policymakers and scientists.
• In a recent survey, 75% of people suggested they would prefer to listen to an interesting story than read it.

Step 1 Upload your science paper
Step 2 SciPod script written
Step 3 Voice audio recorded
Step 4 SciPod published