Dr Chen Zhao | Dr Qianze Dong – The Fine Mechanics of Haematopoiesis
Original Article Reference
This SciPod is a summary of the paper ‘The Fine Mechanics of Haematopoiesis ’ https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-018-1614-y
Share Episode
About this episode
Haematopoiesis is the process through which cellular blood components are produced. It starts during embryonic development to ensure the production of blood cells such as erythrocytes (red cells), leukocytes (white cells), and platelets and continues throughout our lives. All blood cells derive from haematopoietic stem cells located in the bone marrow and, unfortunately, blood cancers may occur during this process. Whether blood cells become inefficient or grow excessively, the outcomes are usually devastating. Dr Chen Zhao (University of Iowa) and Dr Qianze Dong (China Medical University) are exploring the cellular mechanisms of haematopoietic stem cells.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. 
What does this mean?
Share: You can copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
Adapt: You can change, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
Credit: You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made.
Related episodes
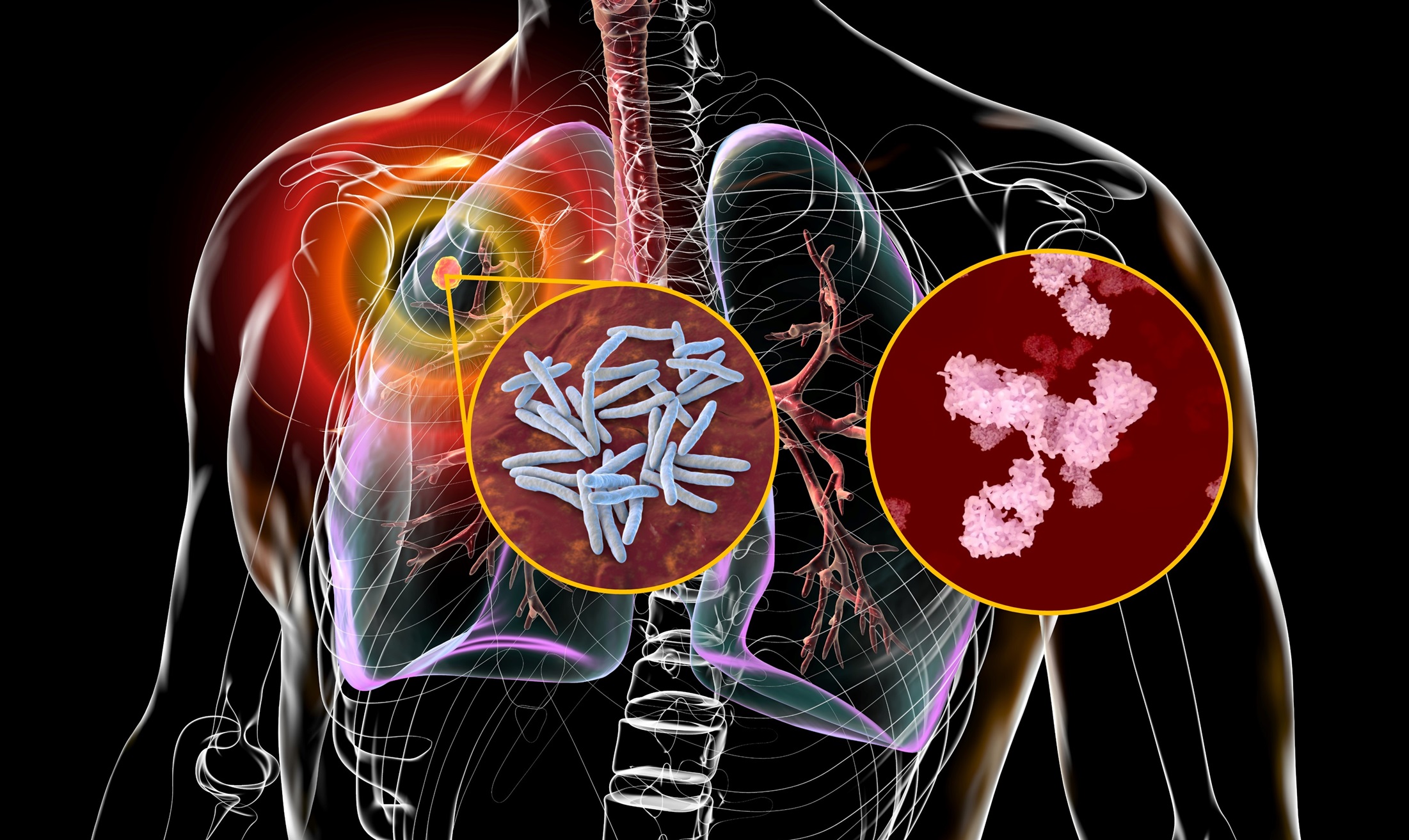
Professor Lobelia Samavati | Paving the Way for Antibody-based Diagnostics for Tuberculosis and Sarcoidosis
Tuberculosis – or TB – is a global health threat, with 10 million new cases annually. Diagnosing TB can be a challenge, as there is a lack of rapid, point-of-care diagnostic tests. It can also be difficult to distinguish between TB and other inflammatory diseases, such as Sarcoidosis. One option may be to identify antibodies in patient samples that can reveal the presence of TB. However, current antibody tests for TB lack accuracy. Professor Lobelia Samavati and colleagues at the Wanye State University School of Medicine in Michigan are tackling this challenge to cast light on the immune signature of these diseases. Their aim is to develop new diagnostic techniques for TB and Sarcoidosis.
Dr Abayomi Sanusi | Can Faith Institutions Encourage People to Maintain Healthy Blood Pressure?
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common and potentially dangerous condition that increases the risk of many severe medical issues, including heart disease, heart attack, stroke, heart failure, and kidney disease. Dr Abayomi Sanusi, a researcher at the University of York, recently carried out a study exploring how faith-based institutions could encourage their community members to adopt healthy behaviours that can reduce hypertension.
Ria Nishikawara | Exploring How to Improve Healthcare for Patients with Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a relatively common and yet poorly understood condition characterised by chronic diffuse pain and stiffness, chronic fatigue, poor sleep and cognitive difficulties. Ria Nishikawara at the University of British Columbia and her collaborators Dr Izabela Schultz, Dr Lee Butterfield, and John Murray, carried out a study exploring the unique healthcare experiences of patients diagnosed with fibromyalgia. Their aim was to determine what patients found most helpful and how the available services could be improved.
Addressing antimalarial drug resistance in Africa to ensure patients can continue to be saved
We are pleased to be joined by Dorothy Achu, Regional Malaria Adviser, WHO African Region; Aimable Mbituyumuremyi, Director, National Malaria Control Program, Ministry of Health, Rwanda; Adam Aspinall, Senior Director, Access and Product Management, and George Jagoe, Executive Vice-President Medicines for Malaria Venture. To learn about antimalarial drug resistance in Africa to ensure patients can continue to be saved.
Increase the impact of your research
• Good science communication helps people make informed decisions and motivates them to take appropriate and affirmative action.
• Good science communication encourages everyday people to be scientifically literate so that they can analyse the integrity and legitimacy of information.
• Good science communication encourages people into STEM-related fields of study and employment.
• Good public science communication fosters a community around research that includes both members of the public, policymakers and scientists.
• In a recent survey, 75% of people suggested they would prefer to listen to an interesting story than read it.

Step 1 Upload your science paper
Step 2 SciPod script written
Step 3 Voice audio recorded
Step 4 SciPod published