The Health-e Babies App for Socially Disadvantaged Women: Embracing Technology to Improve Health Literacy
Original Article Reference
This SciPod is a summary of the paper ‘The Health-e Babies Appfor antenatal education: Feasibility for socially disadvantaged women’ from PLOS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194337
Share Episode
About this episode
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. 
What does this mean?
Share: You can copy and redistribute the material in any medium
or format
Adapt: You can change, and build upon the material for any
purpose, even commercially.
Credit: You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the
license, and indicate if changes were made.
Related episodes
Professor Pei Wang | Defining AI to Ensure Effective Research and Policymaking
Artificial intelligence – or AI – is receiving increasing attention for its rapid development and potential to change society. Researchers are working hard to develop its capabilities, while regulators are racing to ensure it is managed and governed properly. But what do we mean by AI, and how can we define such a complex term? In a recent paper, Professor Pei Wang at Temple University argues that the lack of an agreed definition makes it difficult for policymakers to assess what AI will be capable of in the near future, or even which kinds of AI are desirable. To combat this, he discusses what makes a robust definition, and suggests his own.
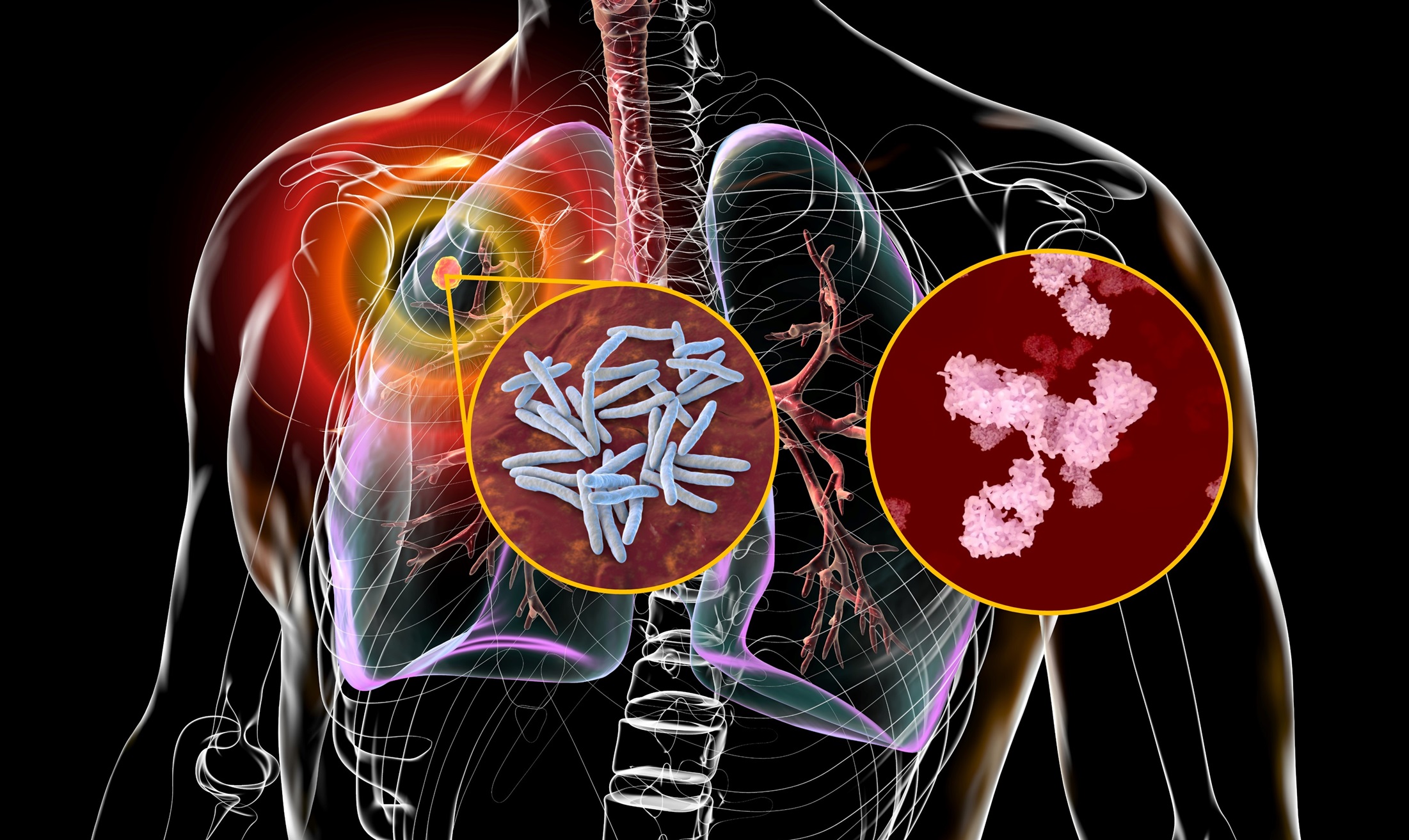
Professor Lobelia Samavati | Paving the Way for Antibody-based Diagnostics for Tuberculosis and Sarcoidosis
Tuberculosis – or TB – is a global health threat, with 10 million new cases annually. Diagnosing TB can be a challenge, as there is a lack of rapid, point-of-care diagnostic tests. It can also be difficult to distinguish between TB and other inflammatory diseases, such as Sarcoidosis. One option may be to identify antibodies in patient samples that can reveal the presence of TB. However, current antibody tests for TB lack accuracy. Professor Lobelia Samavati and colleagues at the Wanye State University School of Medicine in Michigan are tackling this challenge to cast light on the immune signature of these diseases. Their aim is to develop new diagnostic techniques for TB and Sarcoidosis.
Professor Uma Lele | Exploring How India Can Ensure Sustainable Growth and Resilience with Broad Participation into the Future
India has seen impressive economic and institutional growth in recent years, but the country isn’t yet meeting its full potential. In a world that is increasingly volatile and uncertain, how can India overcome its challenges and ensure resilience into the future? In her recent work, Professor Uma Lele explores various ways that India can achieve this.
Professor Ann Nevile | What Evidence Do Policymakers Need to Make Robust Decisions?
Policy decisions are influenced by many factors, from the ideology of the policymaker and their advisors to political expediency. Most would also agree that key political decisions should be evidence-based. However, this is easier said than done. Understanding what evidence policymakers need, and how they should evaluate this, is key for more robust decision-making.
Increase the impact of your research
• Good science communication encourages everyday people to be scientifically literate so that they can analyse the integrity and legitimacy of information.
• Good science communication encourages people into STEM-related fields of study and employment.
• Good public science communication fosters a community around research that includes both members of the public, policymakers and scientists.
• In a recent survey, 75% of people suggested they would prefer to listen to an interesting story than read it.

Upload your science paper
Step 2
SciPod script written
Step 3
Voice audio recorded
Step 4
SciPod published